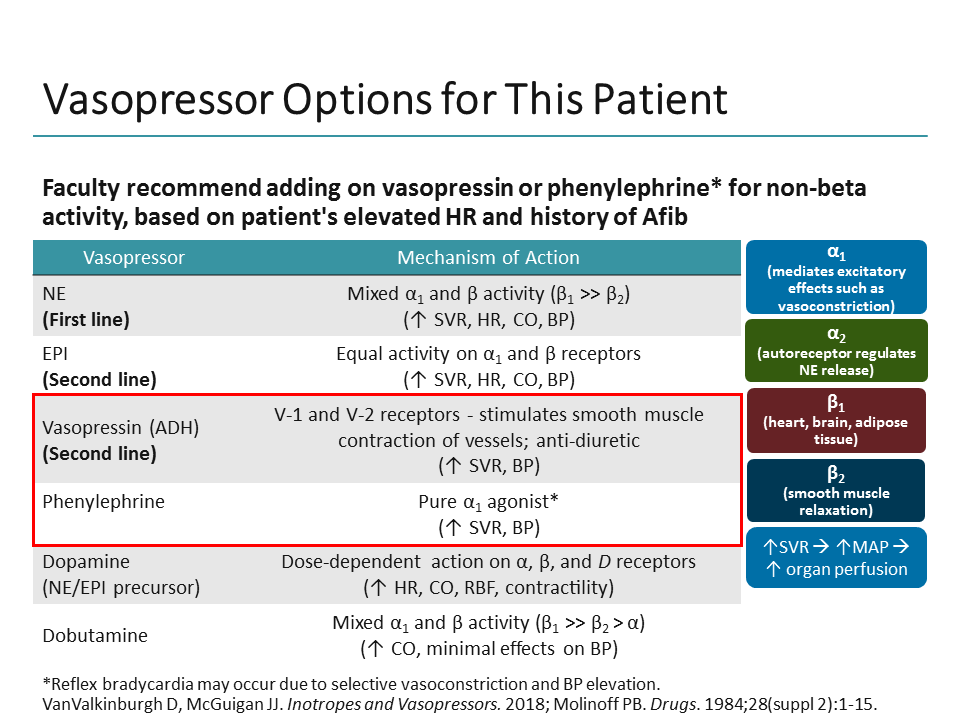
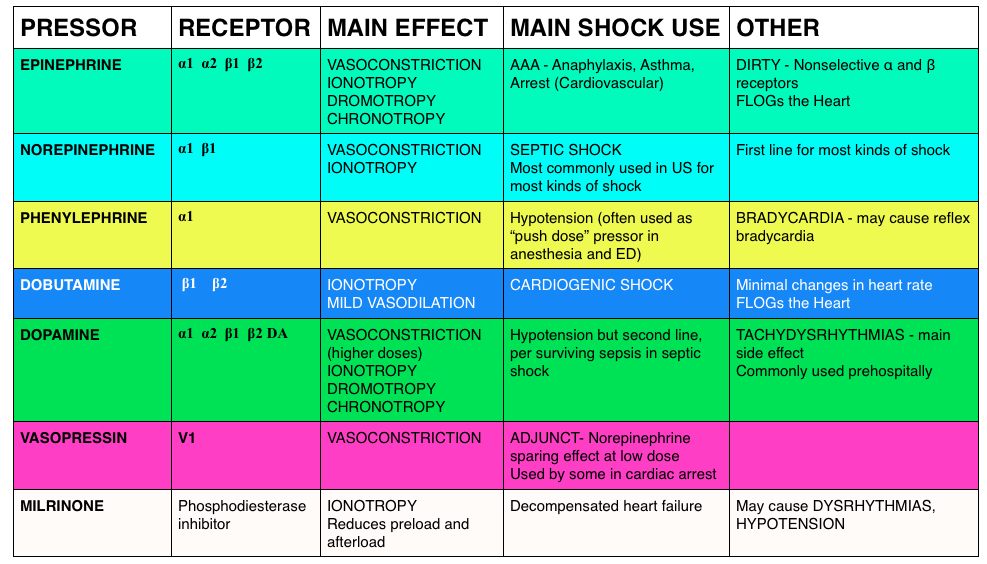
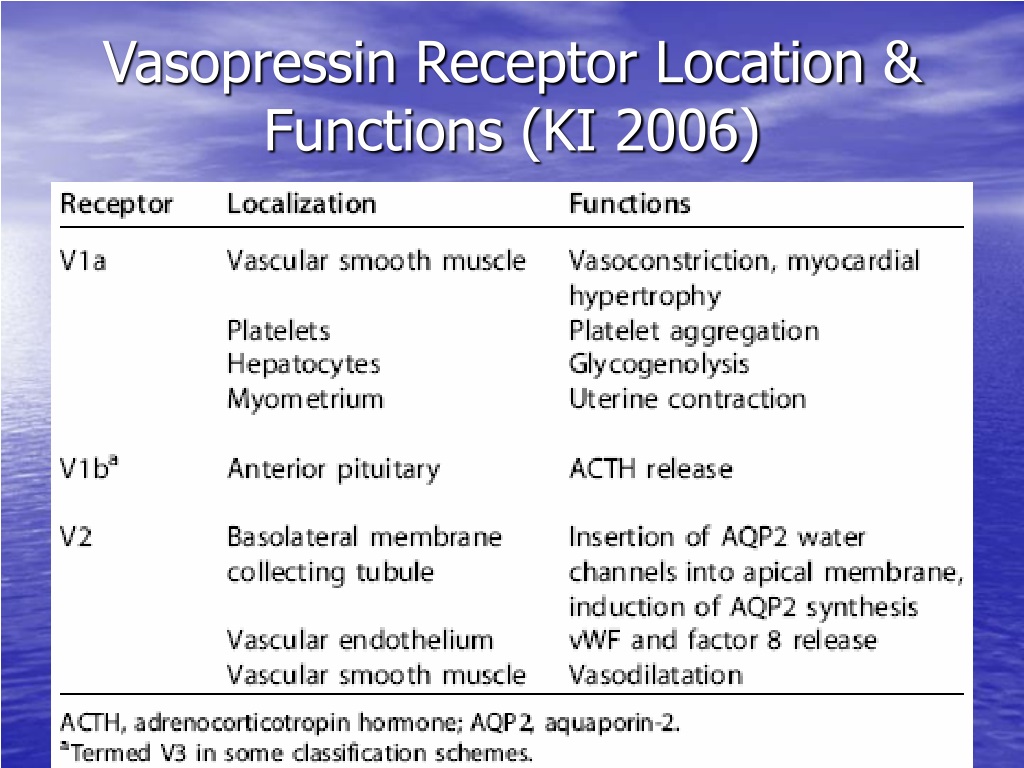
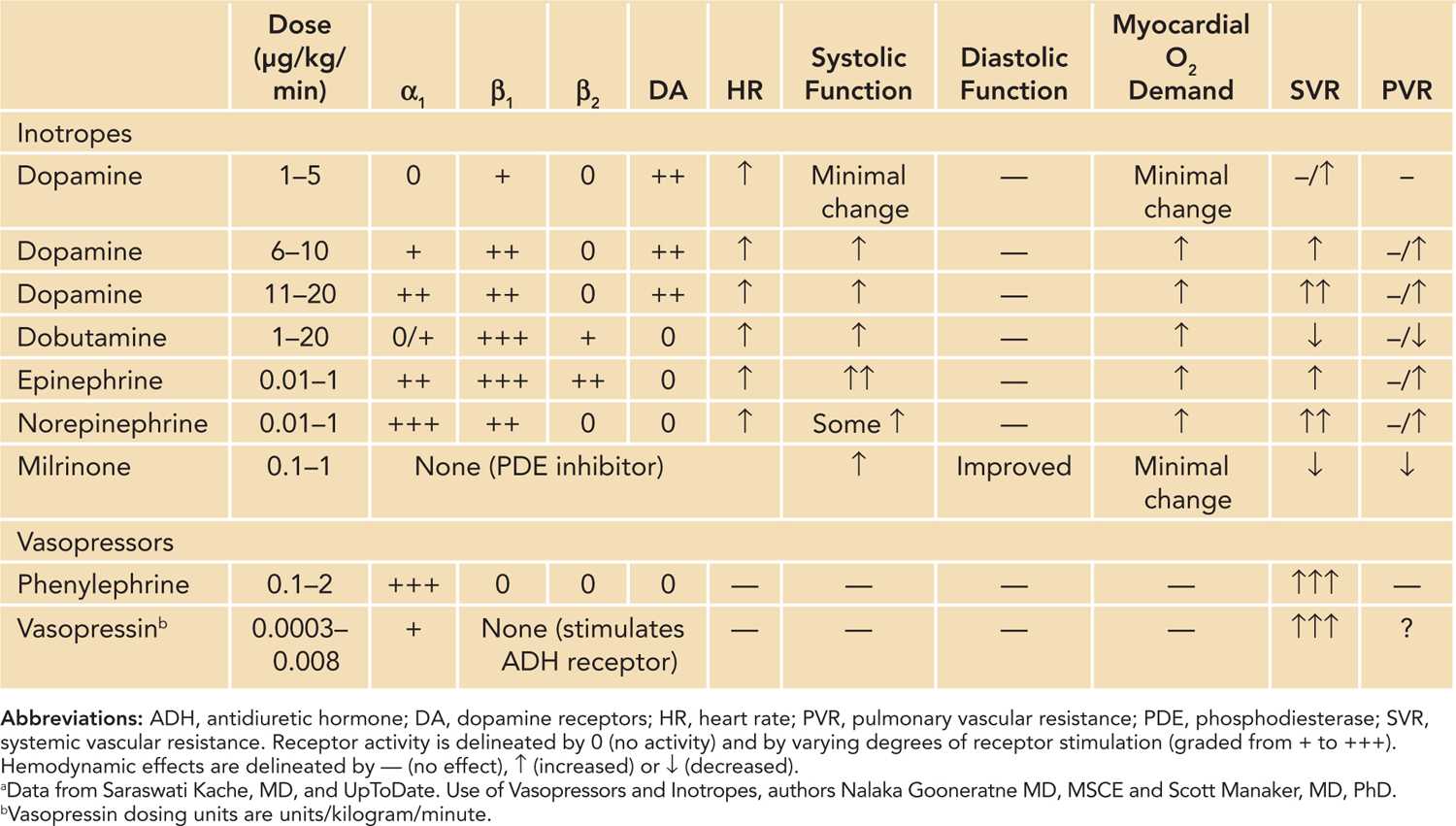
Vasopressor Receptor Chart
Vasopressor Receptor Chart - Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. Cardiogenic shock, typically caused by a heart attack. An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. [1] distributive shock is commonly caused by sepsis,. Norepinephrine is the vasopressor most often used in this scenario. Often, these are people in. Inotropic and vasopressor drug names, clinical indication for therapeutic use, standard dose range, receptor binding (catecholamines), and major clinical side effects However, many drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. A vasopressor is a drug that healthcare providers use to make blood vessels constrict or become narrow in people with low blood pressure. Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. View important safety information, ratings, user reviews, popularity and more. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. Although many vasopressors have been used. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Hemorrhagic shock, which is caused by massive. An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. However, many drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. An overview of inotropes and vasopressors, including their indication, pharmacology, route of administration and cautions. Hemorrhagic shock, which is caused by massive. [1] distributive shock is commonly caused by sepsis,. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. View important safety information, ratings, user reviews, popularity and more. Vasopressors differ from inotropes, which increase cardiac contractility; Norepinephrine is the vasopressor most often used in this scenario. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. Vasopressors differ from inotropes, which increase cardiac contractility; An overview of inotropes and vasopressors, including their indication, pharmacology, route of administration and. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Hemorrhagic shock, which is caused by massive. An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. An overview of inotropes and vasopressors, including their indication, pharmacology, route of administration and cautions. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. [1] distributive shock is commonly caused by sepsis,. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. [1] distributive shock is commonly caused by sepsis,. However, many drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. Often, these are people in. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. Hemorrhagic shock, which is caused by massive. Inotropic and vasopressor drug names, clinical indication for therapeutic use, standard dose range, receptor binding (catecholamines), and major clinical side effects Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. Cardiogenic shock, typically caused by a heart attack. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er. Cardiogenic shock, typically caused by a heart attack. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Most agents exhibit both vasopressor and inotropic effects (figure 1). Often, these are people in. A vasopressor is a drug that healthcare providers use to make blood vessels constrict or become narrow. However, many drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. Vasopressors differ from inotropes, which increase cardiac contractility; Often, these are people in. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels,. Cardiogenic shock, typically caused by a heart attack. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin. Although many vasopressors have been used. Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Contrary to popular belief, there is no such thing as a “front. Dobutamine and milrinone are inotropes. Norepinephrine is the vasopressor most often used in this scenario. Below follows a drug manual for use in the ccu (coronary care unit), icu (intensive care unit) or er (emergency. Vasopressors differ from inotropes, which increase cardiac contractility; Often, these are people in. An overview of inotropes and vasopressors, including their indication, pharmacology, route of administration and cautions. View important safety information, ratings, user reviews, popularity and more. However, many drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. Although many vasopressors have been used. Hemorrhagic shock, which is caused by massive. Inotropic and vasopressor drug names, clinical indication for therapeutic use, standard dose range, receptor binding (catecholamines), and major clinical side effects [1] distributive shock is commonly caused by sepsis,. Options for vasopressor or inopressor include norepinephrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, or vasopressin.Vasopressors and Inotropes Memory Pharm
PPT Vasopressors PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2267617
Vasopressin
Caring for patients receiving vasopressors in the ICU
Vasopressor Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Inotropes and Vasopressors Doses, indications, contraindications and effects
vasopressors FOAMcast
Vasopressor Receptors Chart Printable
PPT Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists Comprehensive Overview For Effective Hyponatremia
Blood Pressure Support Obgyn Key
A Vasopressor Is A Drug That Healthcare Providers Use To Make Blood Vessels Constrict Or Become Narrow In People With Low Blood Pressure.
An Antihypotensive, Also Known As A Vasopressor, Is An Agent That Raises Blood Pressure By Constricting Blood Vessels, Thereby Increasing Systemic Vascular Resistance.
Cardiogenic Shock, Typically Caused By A Heart Attack.
Most Agents Exhibit Both Vasopressor And Inotropic Effects (Figure 1).
Related Post: