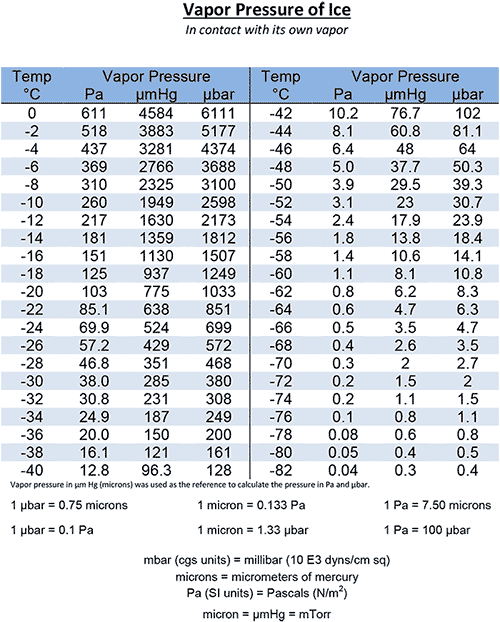
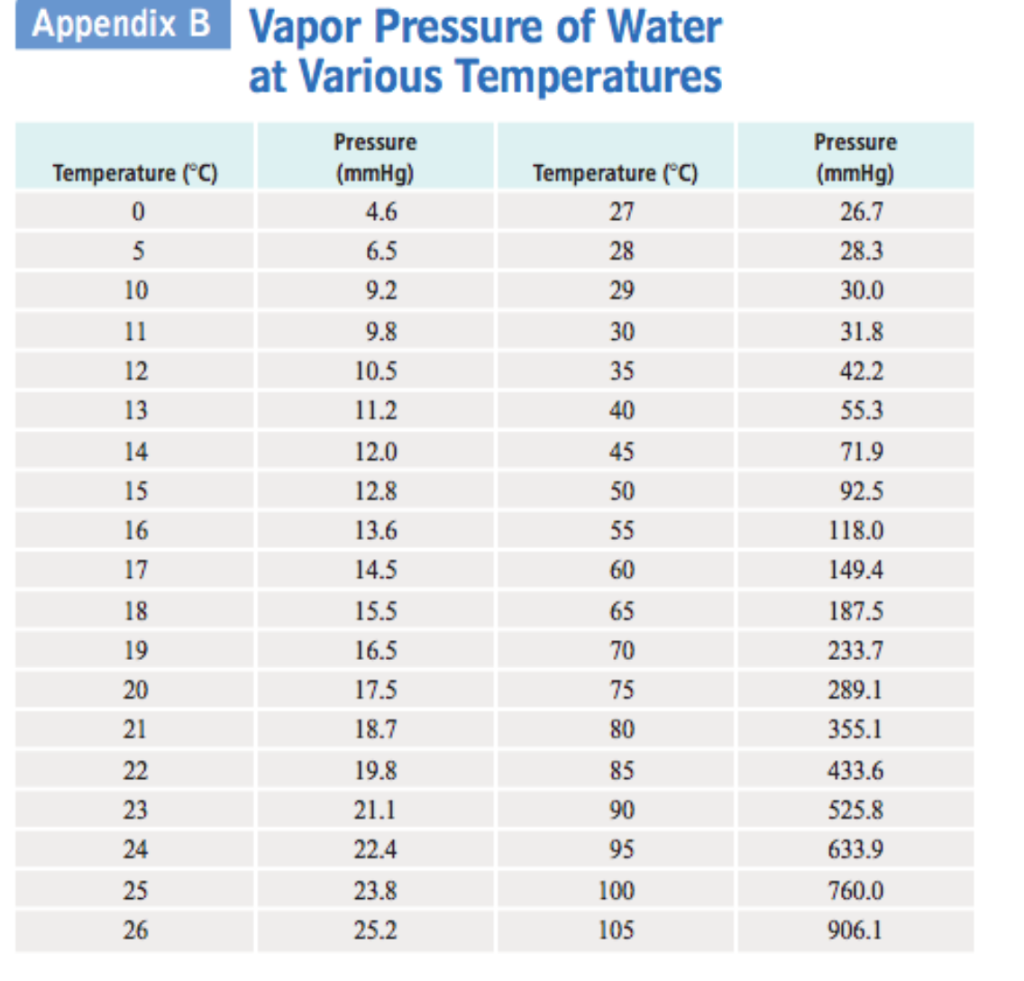
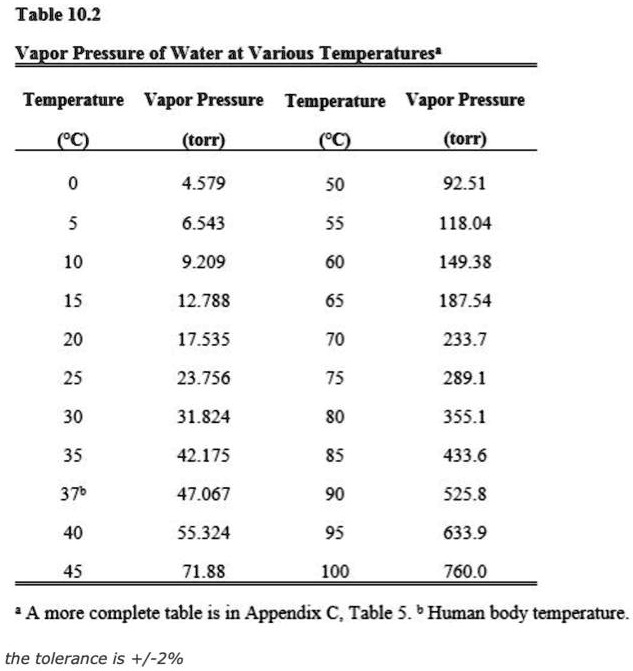
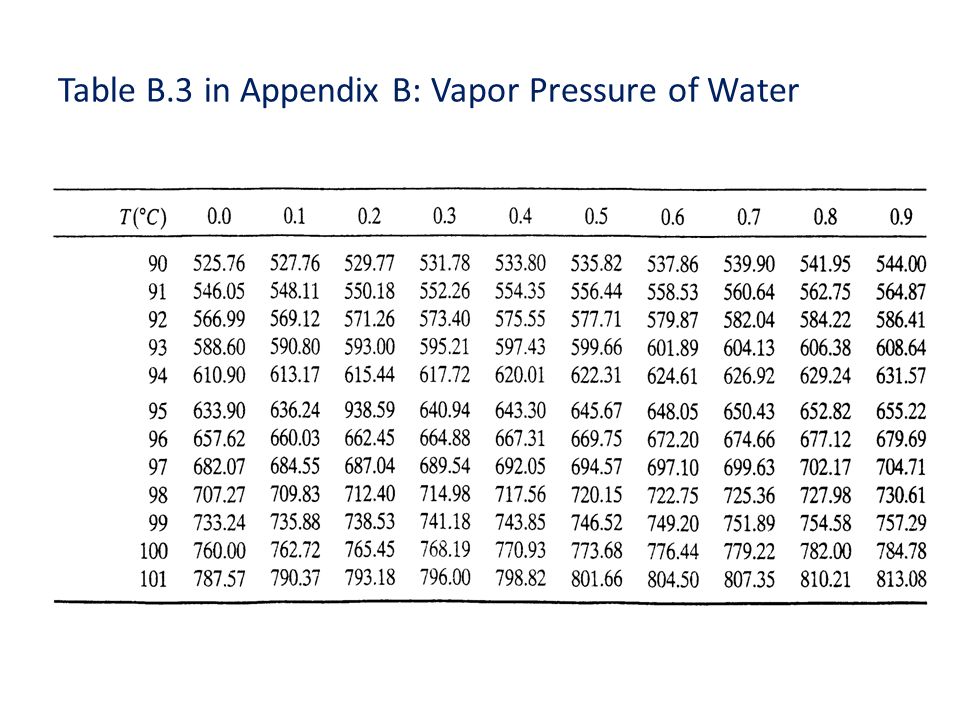
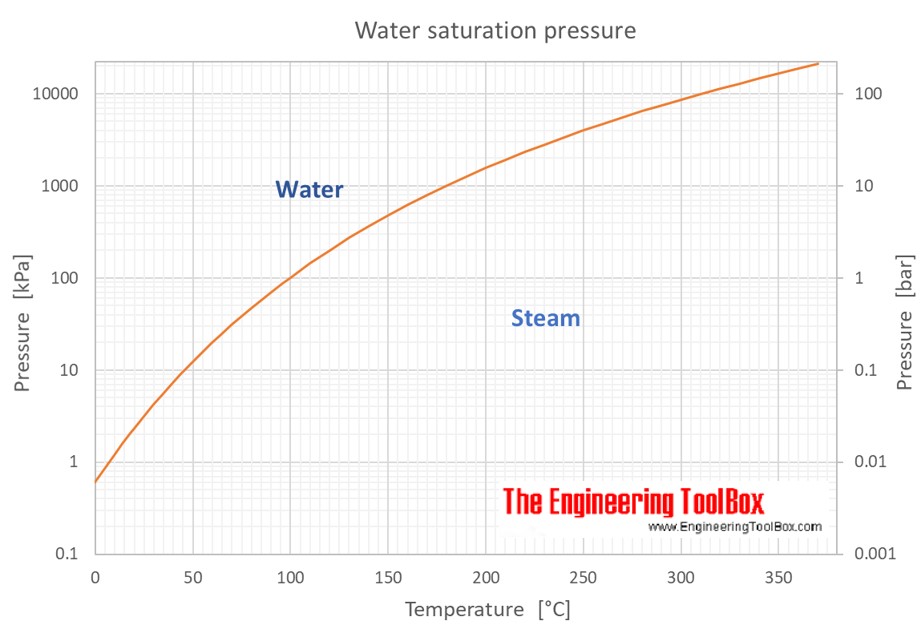
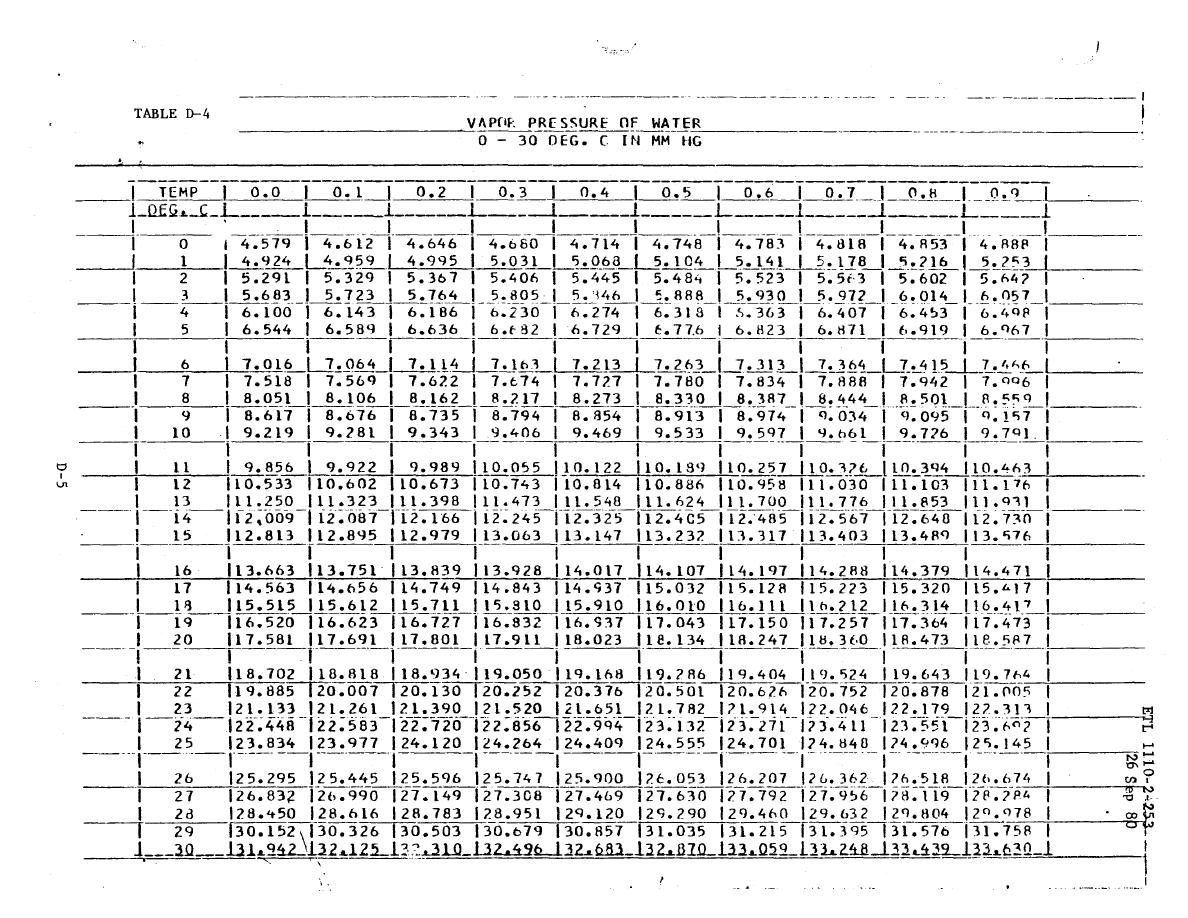
Vapor Pressure Water Chart
Vapor Pressure Water Chart - A vapor is a gas in possible equilibrium with its liquid [or solid] at a temperature below its critical t and either in contact with the liquid or at the equilibrium vapor pressure. A measure of volatility is the vapor pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower. So if we think of air as being nitrogen and oxygen, then there is a partial pressure for nitrogen and a. While gas does not make such an. It is assumed that the vapor of a given compound/element is the gas phase of the same pure. Water has a boiling point of 100 °c. The definition of boiling point is, the temperature which the liquid substance's saturated vapor. I need clarity on saturated vapour pressure in a closed system at equilibrium. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature. 14 octane has a boiling point of 120 °c. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. So if we think of air as being nitrogen and oxygen, then there is a partial pressure for nitrogen and a. The definition of boiling point is, the temperature which the liquid substance's saturated vapor. Vapor implies the existence of a condensed phase that is the source or destination of the gas, or with which the gas may be in equilibrium; Water has a boiling point of 100 °c. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower. I need clarity on saturated vapour pressure in a closed system at equilibrium. When a substance's multiple phases are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other the vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor existing above a liquid surface. A vapor is a gas in possible equilibrium with its liquid [or solid] at a temperature below its critical t and either in contact with the liquid or at the equilibrium vapor pressure. The ∆g is zero at its boiling point (the thermodynamic definition of boiling point), and becomes positive at temperatures below the boiling point. How does saturated vapour pressure relate to vapour pressure? A measure of volatility is the vapor pressure. I need clarity on saturated vapour pressure in a closed system at equilibrium. While gas does not make such an. When a substance's multiple phases are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other the vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor existing above a liquid surface. How does saturated vapour pressure relate to vapour pressure? What is the difference between smell/odor and vapor of a substance? A measure of volatility is the vapor pressure. 14 octane has a boiling. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. A measure of volatility is the vapor pressure. 14 octane has a boiling point of 120 °c. While gas does not make such an. There is a very related term partial pressure. However every liquid has a. 14 octane has a boiling point of 120 °c. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature. A measure of volatility is the vapor pressure. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature. Vapor implies the existence of a condensed phase that is the source or destination of the gas, or with which the gas may be in equilibrium; At a given temperature, a substance with. 14 octane has a boiling point of 120 °c. How does saturated vapour pressure relate to vapour pressure? I need clarity on saturated vapour pressure in a closed system at equilibrium. Water has a boiling point of 100 °c. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. There is a very related term partial pressure. What is the difference between smell/odor and vapor of a substance? Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. The ∆g is zero at its boiling point (the thermodynamic definition of boiling point), and becomes positive at temperatures below the boiling point. Water has a boiling point of 100 °c. A vapor is a gas in possible equilibrium with its liquid [or solid] at a temperature below its critical t and either in contact with the liquid or at the equilibrium vapor pressure. There is a very related term partial pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower.. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature. However every liquid has a. What is the difference between smell/odor and vapor of a substance? Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. While gas does not make such an. A vapor is a gas in possible equilibrium with its liquid [or solid] at a temperature below its critical t and either in contact with the liquid or at the equilibrium vapor pressure. The ∆g is zero at its boiling point (the thermodynamic definition of boiling point), and becomes positive at temperatures below the boiling point. I need clarity on. Water has a boiling point of 100 °c. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature. However every liquid has a. What is the difference between smell/odor and vapor of a substance? There is a very related term partial pressure. When a substance's multiple phases are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other the vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor existing above a liquid surface. So if we think of air as being nitrogen and oxygen, then there is a partial pressure for nitrogen and a. While gas does not make such an. I need clarity on saturated vapour pressure in a closed system at equilibrium. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. A vapor is a gas in possible equilibrium with its liquid [or solid] at a temperature below its critical t and either in contact with the liquid or at the equilibrium vapor pressure. How does saturated vapour pressure relate to vapour pressure? 14 octane has a boiling point of 120 °c. The definition of boiling point is, the temperature which the liquid substance's saturated vapor. Vapor implies the existence of a condensed phase that is the source or destination of the gas, or with which the gas may be in equilibrium;What Is Vapor Pressure Ice at Bev Wood blog
Isohexane Vapor Pressure
Vapor Pressure Of Water Chart
SOLVED Table 10.2 Vapor Pressure of Water at Various Temperatures Temperature (°C) Vapor
Water Vapor Pressure Chart Ponasa
Water Vapor Pressure Chart
Water Vapor Saturation Pressure Data, Tables & Calculator
Water Vapor Pressure Chart
Water activity and vapour pressure values. Download Table
Vapor Pressure Of Water Chart
A Measure Of Volatility Is The Vapor Pressure.
It Is Assumed That The Vapor Of A Given Compound/Element Is The Gas Phase Of The Same Pure.
At A Given Temperature, A Substance With Higher Vapor Pressure Vaporizes More Readily Than A Substance With A Lower.
The ∆G Is Zero At Its Boiling Point (The Thermodynamic Definition Of Boiling Point), And Becomes Positive At Temperatures Below The Boiling Point.
Related Post: