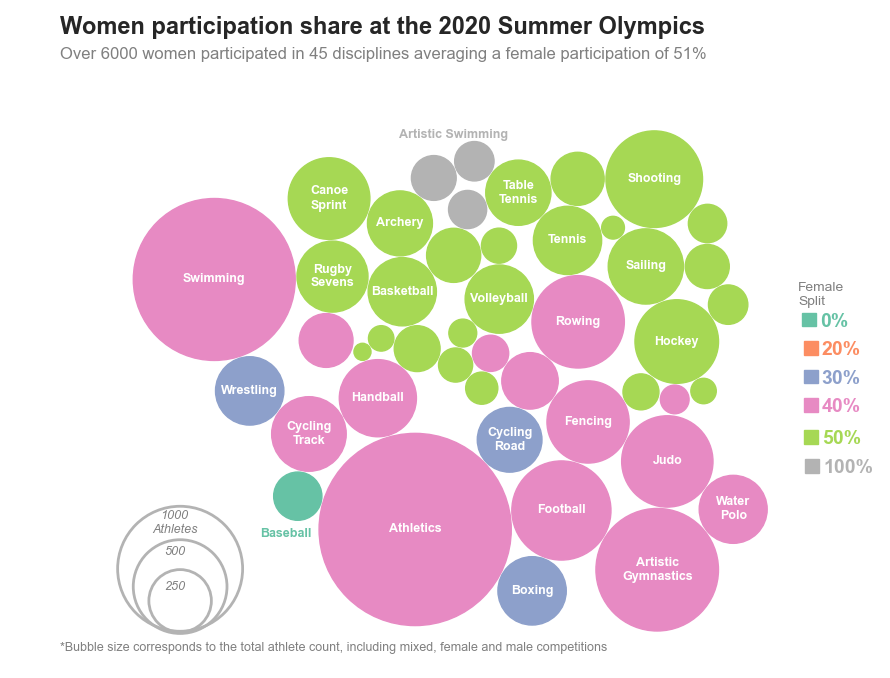
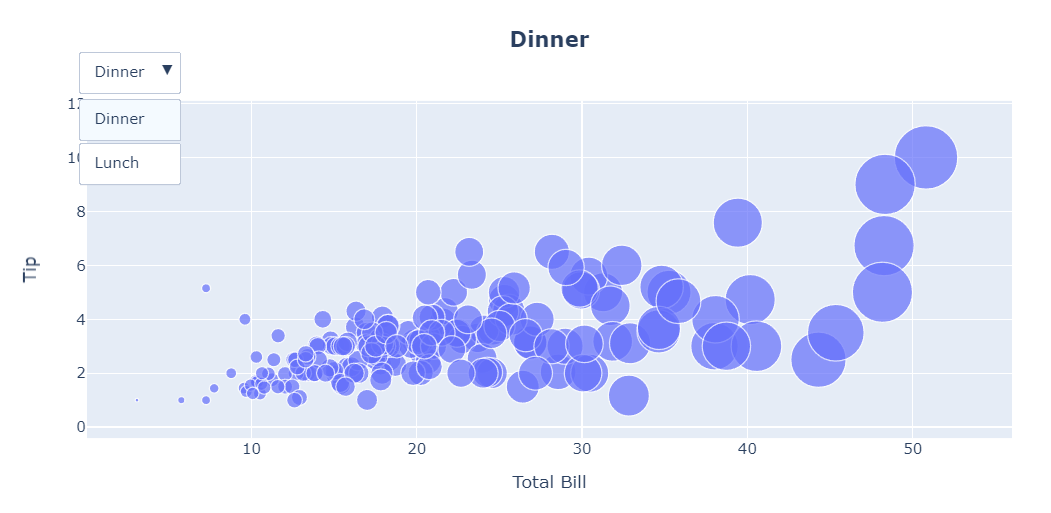
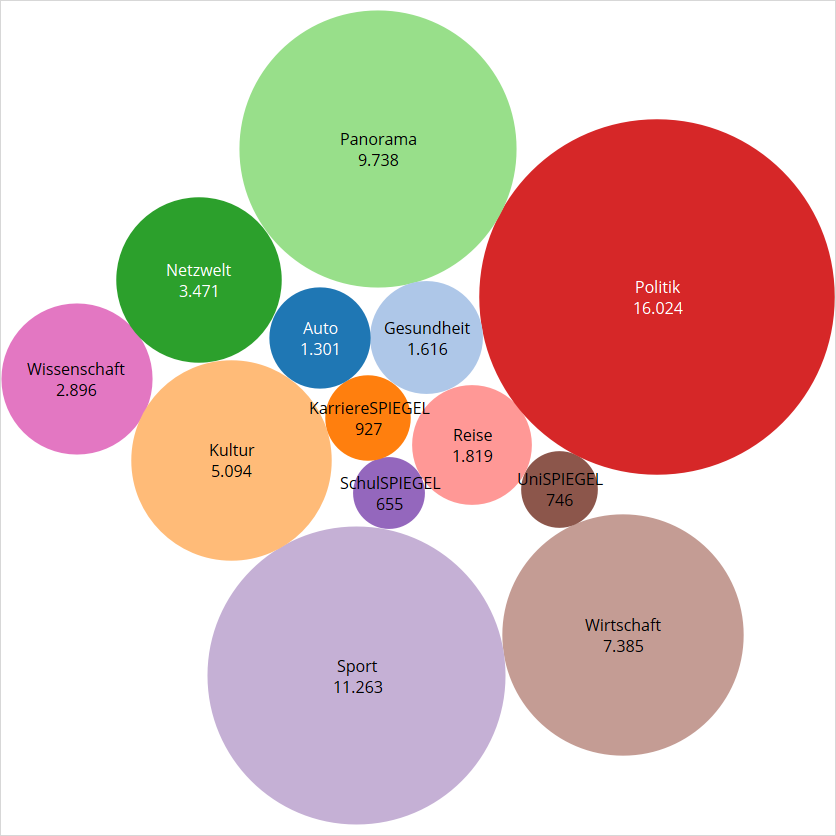
Python Bubble Chart
Python Bubble Chart - 1 you can use the != operator to check for inequality. In python this is simply =. Unary arithmetic and bitwise/binary operations and. 96 what does the “at” (@) symbol do in python? Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3+ every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. In python there is id function that shows. This underscoring seems to occur a lot, and i was wondering if this was a requirement in the python language, or merely a matter of convention? Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to make that method do something not related to xor. In python 2.2 or later in the 2.x line, there is no difference for integers unless you perform a from __future__ import division, which causes python 2.x to adopt the 3.x behavior. In python this is simply =. In python 2.2 or later in the 2.x line, there is no difference for integers unless you perform a from __future__ import division, which causes python 2.x to adopt the 3.x behavior. To translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm. I know that i can use something like string[3:4] to get a substring in python, but what does the 3 mean in somesequence[::3]? This underscoring seems to occur a lot, and i was wondering if this was a requirement in the python language, or merely a matter of convention? 1 you can use the != operator to check for inequality. In python there is id function that shows. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to make that method do something not related to xor. Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3+ every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. This underscoring seems to occur a lot, and i was wondering if this was a requirement in the python language, or merely a matter of convention? Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to make that method do something not. In python this is simply =. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. Moreover in python 2 there was <> operator which used to do the same thing, but it has been deprecated in python 3. Unary arithmetic and bitwise/binary operations and. To translate this pseudocode into. Moreover in python 2 there was <> operator which used to do the same thing, but it has been deprecated in python 3. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to make that method do something not related to xor.. To translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm. Moreover in python 2 there was <> operator which used to do the same thing, but it has been deprecated in python 3. In python there is id function that shows. Side note, seeing as python defines. In python there is id function that shows. To translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm. This underscoring seems to occur a lot, and i was wondering if this was a requirement in the python language, or merely a matter of convention? @ symbol is. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. In python this is simply =. Unary arithmetic and bitwise/binary operations and. In python there is id function that shows. 1 you can use the != operator to check for inequality. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. To translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor. In python 2.2 or later in the 2.x line, there is no difference for integers unless you perform a from __future__ import division, which causes python 2.x to adopt the 3.x behavior. Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3+ every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. In python. In python 2.2 or later in the 2.x line, there is no difference for integers unless you perform a from __future__ import division, which causes python 2.x to adopt the 3.x behavior. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to. To translate this pseudocode into python you would need to know the data structures being referenced, and a bit more of the algorithm. Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3+ every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation. I know that i can use something like string[3:4] to get a substring in python, but what does the 3 mean in somesequence[::3]? Since is for comparing objects and since in python 3+ every variable such as string interpret as an object, let's see what happened in above paragraphs. In python 2.2 or later in the 2.x line, there is no difference for integers unless you perform a from __future__ import division, which causes python 2.x to adopt the 3.x behavior. Moreover in python 2 there was <> operator which used to do the same thing, but it has been deprecated in python 3. In python there is id function that shows. Unary arithmetic and bitwise/binary operations and. Side note, seeing as python defines this as an xor operation and the method name has xor in it, i would consider it a poor design choice to make that method do something not related to xor. @ symbol is a syntactic sugar python provides to utilize decorator, to paraphrase the question, it's exactly about what does. 96 what does the “at” (@) symbol do in python? In python this is simply =. This underscoring seems to occur a lot, and i was wondering if this was a requirement in the python language, or merely a matter of convention?Bubble chart using Plotly in Python
Create a Moving Bubbles Chart in Python by Avi Chawla
matplotlib How to draw a Circle shaped packed Bubble Chart in Python? Stack Overflow
The Glowing Python How to make Bubble Charts with matplotlib
Python Bubble Chart Examples with Code
Matplotlibpyplotpsd In Python
I found a hidden gem in Matplotlib’s library Packed Bubble Charts in Python by Anna Gordun
Create Interactive Bubble Charts using Plotly in Python ML Hive
Bubble Charts in Python (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly) by Okan Yenigün Towards Dev
How To Plot A Circle In Python Using Matplotlib Images
Using Or In If Statement (Python) [Duplicate] Asked 7 Years, 5 Months Ago Modified 8 Months Ago Viewed 149K Times
To Translate This Pseudocode Into Python You Would Need To Know The Data Structures Being Referenced, And A Bit More Of The Algorithm.
1 You Can Use The != Operator To Check For Inequality.
Related Post: