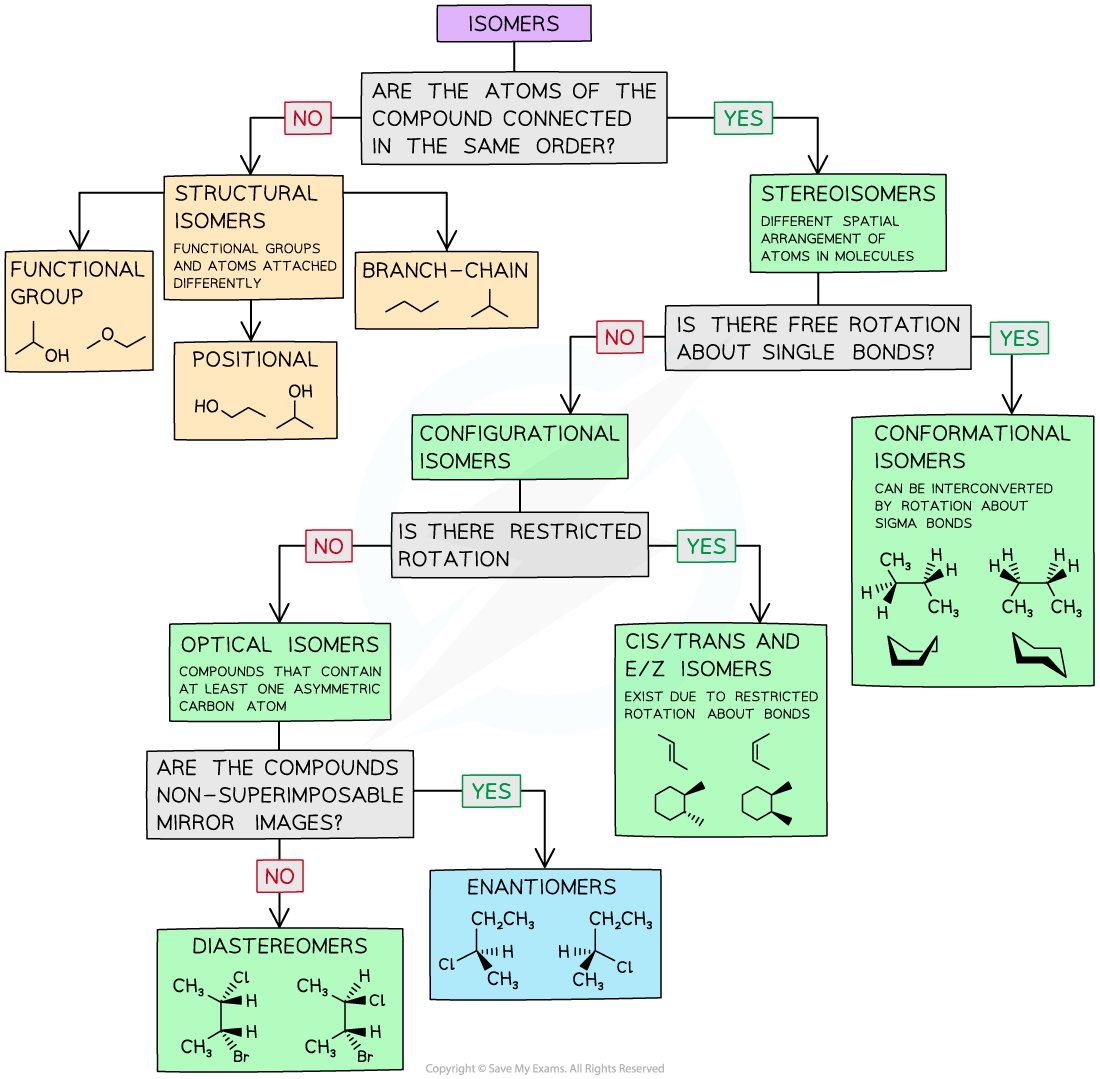
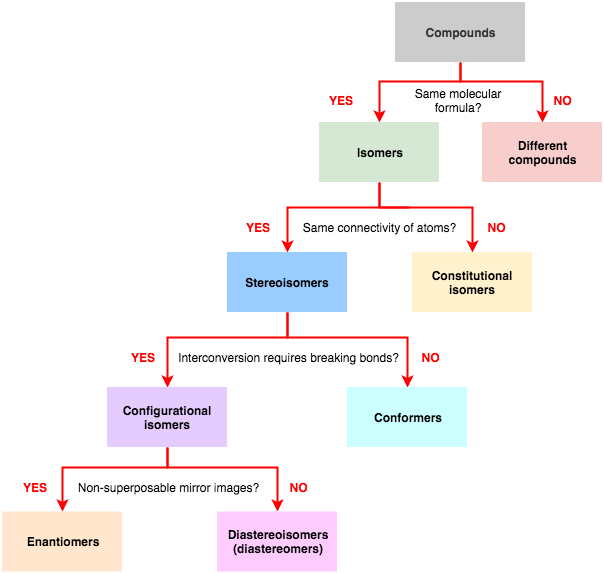
Isomer Flow Chart
Isomer Flow Chart - In both molecules, the bonding order. How do isomers differ from one another. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of propanol, as well as the isomer methoxyethane. What are their different types. 同分異構物 (isomer)简称 异构体[3],是擁有相同 分子式,但 結構式 卻不相同的多種 分子 或 多原子离子。 其彼此間的化學性質並不相同,除非它們擁有相同的 官能团。 The classical example is dichloroethene , specifically the structural isomer that has one chlorine bonded to each carbon. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. It must lie in an energy well. There are two general types of isomers. There are two general types of isomers. Constitutional isomers are molecules of different. The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of propanol, as well as the isomer methoxyethane. In both molecules, the bonding order. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; The classical example is dichloroethene , specifically the structural isomer that has one chlorine bonded to each carbon. Isomers are molecules with the same atoms but arranged in different ways, giving them unique properties. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. Isomers are molecules with the same atoms but arranged in different ways, giving them unique properties. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; There are two general types of isomers. The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of propanol, as well as. It must lie in an energy well. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; 同分異構物 (isomer)简称 异构体[3],是擁有相同 分子式,但 結構式 卻不相同的多種 分子 或 多原子离子。 其彼此間的化學性質並不相同,除非它們擁有相同的 官能团。 The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. Isomers are molecules with the same. There are two general types of isomers. Isomers are molecules with the same atoms but arranged in different ways, giving them unique properties. It must lie in an energy well. In both molecules, the bonding order. Constitutional isomers are molecules of different. How do isomers differ from one another. The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. Isomers are molecules with the same atoms but arranged in different ways, giving them unique properties. What are their different types. The classical example is. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. The classical example is dichloroethene , specifically the structural isomer that has one chlorine bonded to each carbon. It has two conformational. 同分異構物 (isomer)简称 异构体[3],是擁有相同 分子式,但 結構式 卻不相同的多種 分子 或 多原子离子。 其彼此間的化學性質並不相同,除非它們擁有相同的 官能团。 How do isomers differ from one another. There are two general types of isomers. What are their different types. Constitutional isomers are molecules of different. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. In both molecules, the bonding order. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; Check out a few examples, along with structures and diagrams. How do isomers differ from one another. The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of propanol, as well as the isomer methoxyethane. Isomers are molecules with the. It must lie in an energy well. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. The classical example is dichloroethene , specifically the structural isomer that has one chlorine bonded to each carbon. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. It must lie in an energy well. How do isomers differ from one another. Structural isomers differ in how atoms are joined, while stereoisomers. Check out a few examples, along with structures and diagrams. It has two conformational isomers, with the two chlorines on the same. The chemical structure, c 3 h 8 o exists as several isomers of propanol, as well as the isomer methoxyethane. The classical example is dichloroethene , specifically the structural isomer that has one chlorine bonded to each carbon. 同分異構物 (isomer)简称 异构体[3],是擁有相同 分子式,但 結構式 卻不相同的多種 分子 或 多原子离子。 其彼此間的化學性質並不相同,除非它們擁有相同的 官能团。 Check out a few examples, along with structures and diagrams. In both molecules, the bonding order. Constitutional isomers are molecules of different. What are their different types. It must lie in an energy well. Finally, an isomer must be an energy minimum; Isomers are molecules with the same atoms but arranged in different ways, giving them unique properties. There are two general types of isomers.Ch 7 Isomer types Teaching chemistry, Organic chemistry, Study chemistry
describing the type of isomer Organic chemistry help, Chemistry classroom, Organic chemistry
Summary Organic Chemistry 1 Textbook Wize
Isomer Flowchart — Making Molecules
1.5 Isomerism Chemistry LibreTexts
IB DP Chemistry HL复习笔记20.3.1 Stereoisomers翰林国际教育
Isomer Flowchart — Making Molecules
8.1 Types of Isomers Chemistry LibreTexts
Isomerism Flowchart
Isomer Flow Chart Portal.posgradount.edu.pe
The Cis Isomer Has The Two Single Hydrogen Atoms On The Same Side Of The Molecule, While The Trans Isomer Has Them On Opposite Sides Of The Molecule.
How Do Isomers Differ From One Another.
Structural Isomers Differ In How Atoms Are Joined, While Stereoisomers.
Related Post: