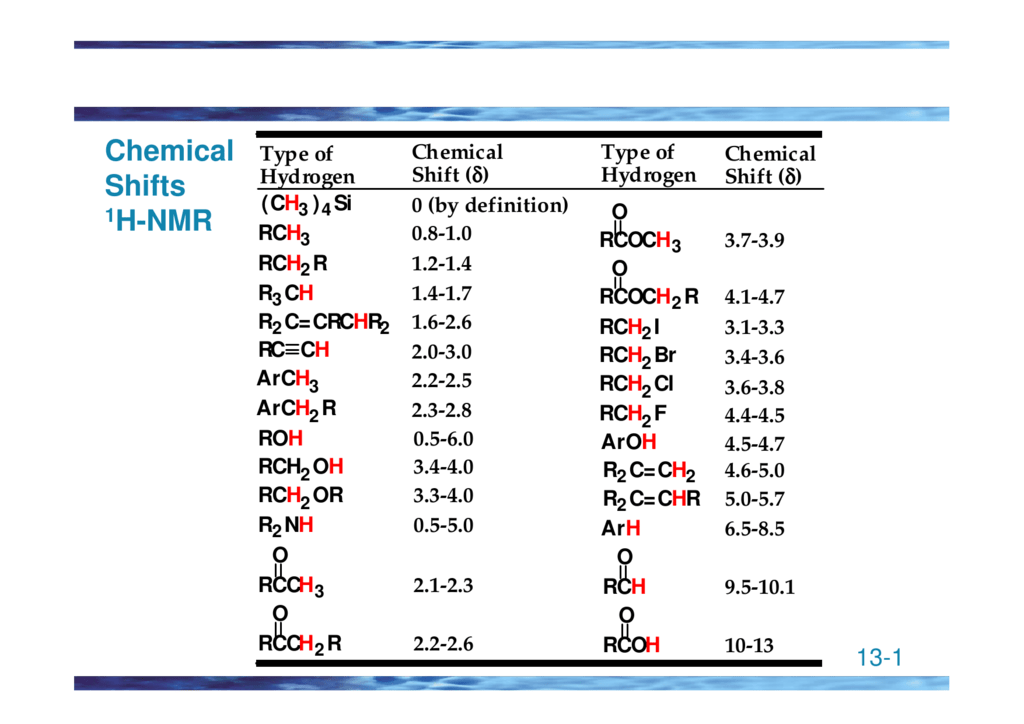
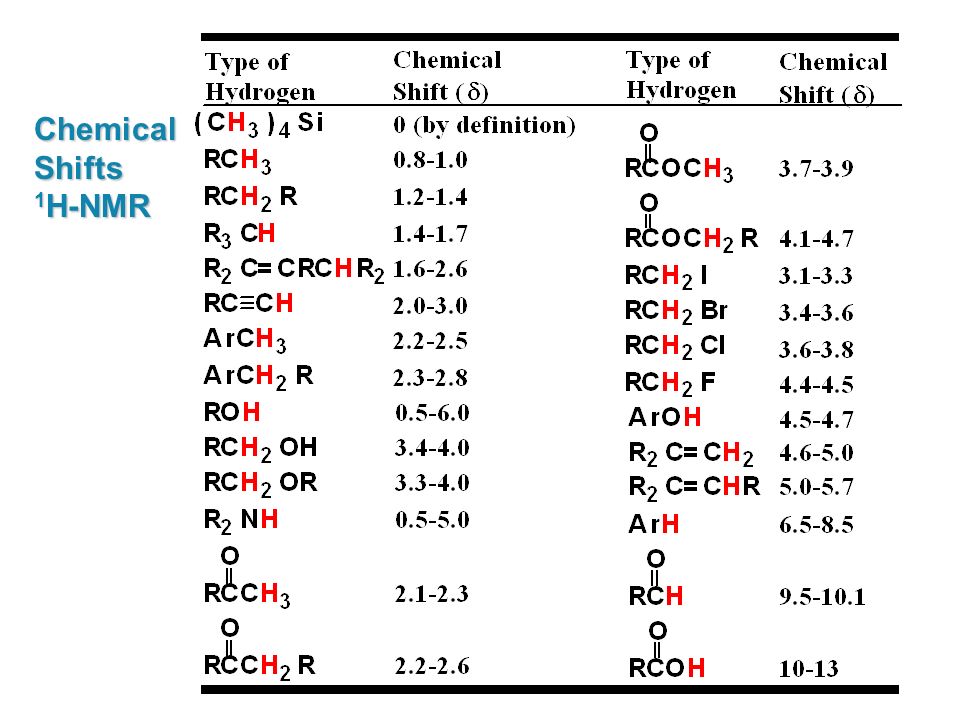
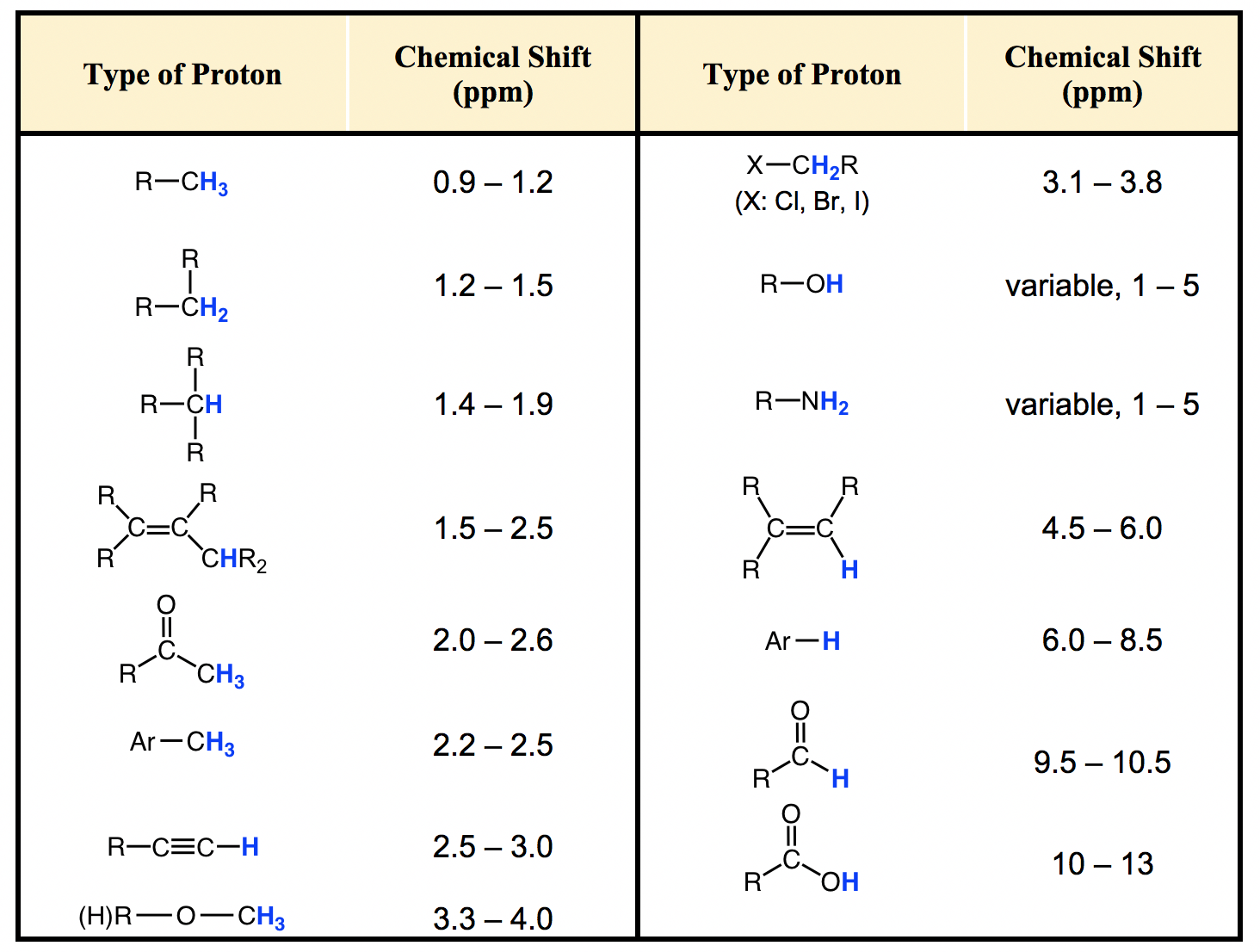
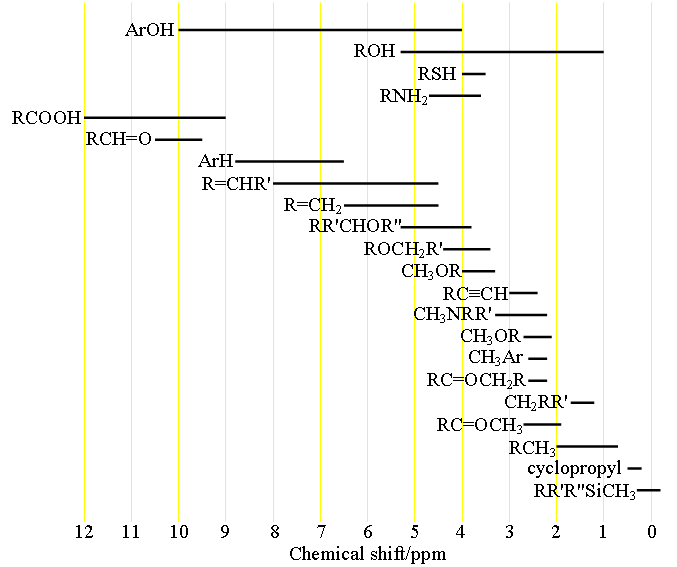
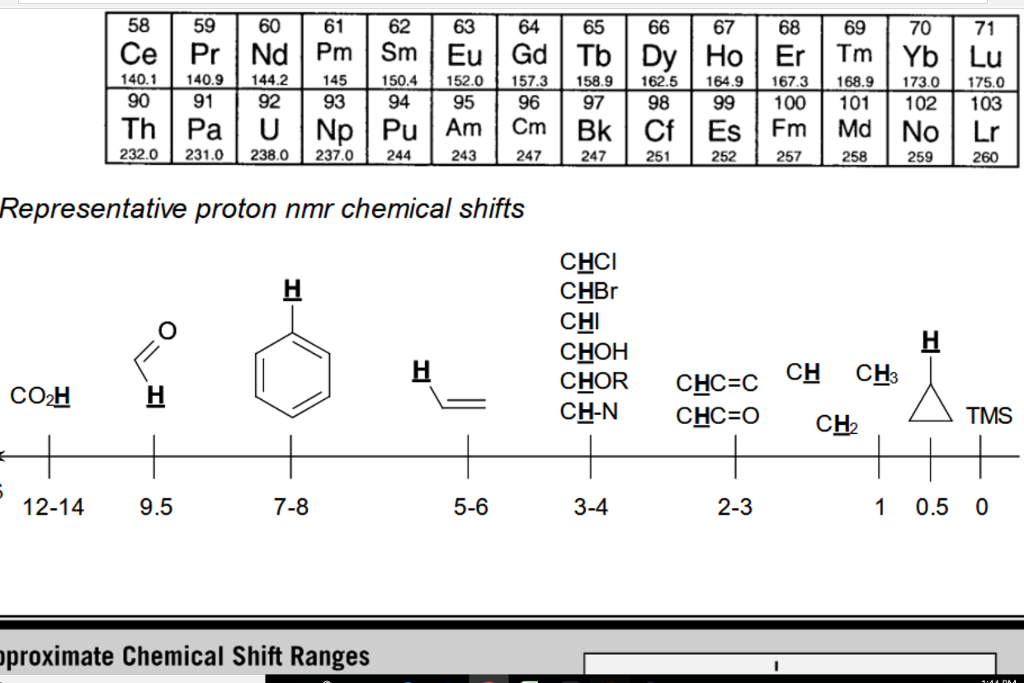
H Nmr Chart
H Nmr Chart - Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts. You can download this chart as a printable acrobat pdf file. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts note: It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of. Nmr chemical shift and ppm value chart. In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an nmr signal at +22.2 ppm, the adjacent methylene protons (blue) give a signal at +12.6 ppm, and the methyl. The effect of electronegativity and magnetic anisotropy on protons in upfield and downfield regions. A guide to 1h nmr chemical shift values nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) is a commonly used technique for organic compound structure determination. The effect of electronegativity and magnetic anisotropy on protons in upfield and downfield regions. You can download this chart as a printable acrobat pdf file. A guide to 1h nmr chemical shift values nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) is a commonly used technique for organic compound structure determination. From table 14.4 (labbook) or table h.6 (spec book) substituted alkanes 1. Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. Alkene region modified from earlier handout Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts note: If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an nmr signal at +22.2 ppm, the adjacent methylene protons (blue) give a signal at +12.6 ppm, and the methyl. Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts. You can download this chart as a printable acrobat pdf file. If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts. Overview of typical. Alkene region modified from earlier handout If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts. Understanding the basics of nmr theory gets us ready to move on to the. Alkene region modified from earlier handout In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an nmr signal at +22.2 ppm, the adjacent methylene protons (blue) give a signal at +12.6 ppm, and the methyl. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. From table 14.4 (labbook) or table h.6 (spec book). In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an nmr signal at +22.2 ppm, the adjacent methylene protons (blue) give a signal at +12.6 ppm, and the methyl. From table 14.4 (labbook) or table h.6 (spec book) substituted alkanes 1. Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts. It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an nmr signal at +22.2 ppm, the adjacent methylene protons (blue) give a signal at +12.6 ppm, and the methyl. From table 14.4 (labbook) or table h.6 (spec book) substituted alkanes 1. Here we present. Here we present the nmr shifts of the most commonly used solvents and impurities in organic synthesis measured in the 7 most frequently used deuterated solvents. Nmr chemical shift and ppm value chart. It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of. In the nmr spectrum of the dianion, the innermost methylene protons (red) give an. Understanding the basics of nmr theory gets us ready to move on to the most important and practical part in this section, that is how to understand the 1h nmr spectrum and elucidate the. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. You can download this chart as a printable acrobat pdf file. From table 14.4. Nmr chemical shift and ppm value chart. It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of. Alkene region modified from earlier handout Understanding the basics of nmr theory gets us ready to move on to the most important and practical part in this section, that is how to understand the 1h nmr spectrum and elucidate the.. Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts. If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. The effect of electronegativity and magnetic anisotropy on protons in upfield and downfield regions. Understanding the basics of nmr theory. Understanding the basics of nmr theory gets us ready to move on to the most important and practical part in this section, that is how to understand the 1h nmr spectrum and elucidate the. If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will. It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of. A guide to 1h nmr chemical shift values nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) is a commonly used technique for organic compound structure determination. Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts. Nmr chemical shift and ppm value chart. You can download this chart as a printable acrobat pdf file. Understanding the basics of nmr theory gets us ready to move on to the most important and practical part in this section, that is how to understand the 1h nmr spectrum and elucidate the. If a protic deuterated solvent is used (e.g., d2o or cd3od), then the nh and oh protons will exchange with the deuterium and the peaks will shrink or disappear entirely, since d (2h) does. It describes nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) in details relevant to organic chemistry. The effect of electronegativity and magnetic anisotropy on protons in upfield and downfield regions. Alkene region modified from earlier handout Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts note: Overview of typical 1h nmr shifts.Analytical Chemistry A Guide to Proton Nuclear Resonance (NMR) Compound Interest
NMR Spectroscopy Principles, Interpreting an NMR Spectrum and Common Problems Technology Networks
Nmr Shift Chart vrogue.co
H Nmr Chemical Shift Chart Ponasa
H Nmr Spectroscopy Table at Lois Coffman blog
6.6 ¹H NMR Spectra and Interpretation (Part I) Organic Chemistry I
H Nmr Chemical Shift Chart Ponasa
Nmr Values Chart
H Nmr Chemical Shift Chart Ponasa
H Nmr Spectrum Chart
In The Nmr Spectrum Of The Dianion, The Innermost Methylene Protons (Red) Give An Nmr Signal At +22.2 Ppm, The Adjacent Methylene Protons (Blue) Give A Signal At +12.6 Ppm, And The Methyl.
Here We Present The Nmr Shifts Of The Most Commonly Used Solvents And Impurities In Organic Synthesis Measured In The 7 Most Frequently Used Deuterated Solvents.
From Table 14.4 (Labbook) Or Table H.6 (Spec Book) Substituted Alkanes 1.
Related Post: