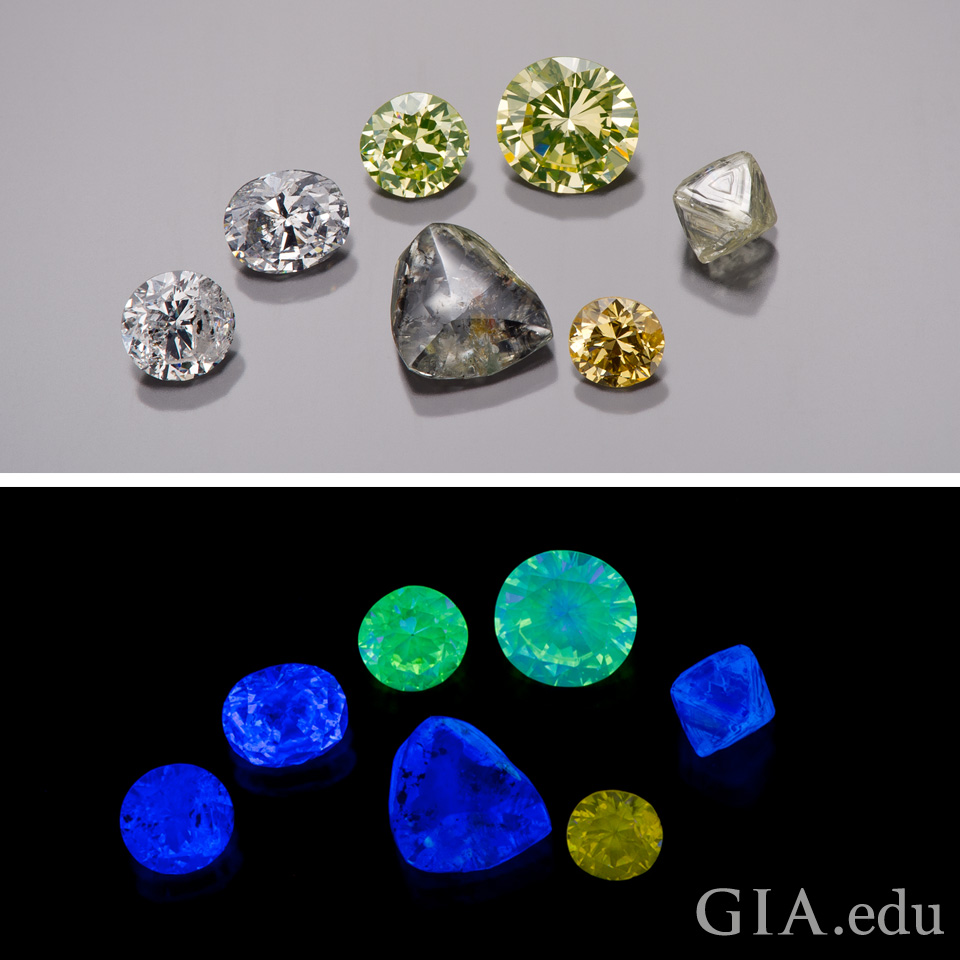
Fluorescence Diamond Chart
Fluorescence Diamond Chart - The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of atoms in a material, which then reemit almost immediately (within about 10 −8 seconds). Fluorescence from simple english wikipedia, the free encyclopedia endothelial cells under the microscope with three separate channels marking specific cellular components fluorescence. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation,. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence that through microscopy allows users to determine the distribution of a single molecule species, its amount and its localization inside a. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence from simple english wikipedia, the free encyclopedia endothelial cells under the microscope with three separate channels marking specific cellular components fluorescence. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence that through microscopy allows users to determine the distribution of a single molecule species, its amount and its localization inside a. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of atoms in a material, which then reemit almost immediately (within about 10 −8 seconds). When exposed to ultraviolet radiation,. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of atoms in a material, which then reemit almost immediately (within about 10 −8 seconds). Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence that through microscopy allows. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence that through microscopy allows users to determine the distribution of a single molecule species, its amount and its localization inside a. Fluorescence, emission of. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of atoms in a material, which then reemit almost immediately (within about 10 −8 seconds). Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. Fluorescence is a form of. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence from simple english wikipedia, the free encyclopedia endothelial cells under the microscope with three separate channels marking specific cellular components fluorescence. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of atoms in a material, which then reemit almost immediately (within about 10 −8 seconds). Fluorescence is a form. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation,. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. Fluorescence, emission of electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, caused by excitation of. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. Fluorescence is a form of luminescence that through microscopy allows users to. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. The specific frequencies of excitation and. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes. The specific frequencies of excitation and. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation,. Fluorescence from simple english wikipedia, the free encyclopedia endothelial cells under the microscope with three separate channels marking specific cellular components fluorescence. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence,. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical. Fluorescence is the ability of certain chemicals to give off visible light after absorbing radiation which is not normally visible, such as ultraviolet light. Fluorescence from simple english wikipedia, the free encyclopedia endothelial cells under the microscope with three separate channels marking specific cellular components fluorescence. Fluorescence occurs when an atom or molecules relaxes through vibrational relaxation to its ground state after being electrically excited. Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. The specific frequencies of excitation and. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation,. Fluorescence is a member of the ubiquitous luminescence family of processes in which susceptible molecules emit light from electronically excited states created by either a physical.The Ultimate Diamond Fluorescence Guide StoneAlgo StoneAlgo
Using Luminescence for Diamond Identification Gemmological Association of Australia
Gemstone Fluorescence Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
What is fluorescence in diamonds? Aureus Boutique
Diamond Fluorescence Definition & Chart Is It Good or Bad? Selecting A Diamond
What is Diamond Fluorescence? Alida Jewelry
Gemstone Fluorescence Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Understanding Diamond Fluorescence Diamond Buzz
Fluorescent Diamond Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Is Diamond Fluorescence Good or Bad? A Comprehensive Guide
Fluorescence, Emission Of Electromagnetic Radiation, Usually Visible Light, Caused By Excitation Of Atoms In A Material, Which Then Reemit Almost Immediately (Within About 10 −8 Seconds).
Fluorescence Is A Form Of Luminescence That Through Microscopy Allows Users To Determine The Distribution Of A Single Molecule Species, Its Amount And Its Localization Inside A.
Related Post: