Fillmore Seating Chart Silver Spring
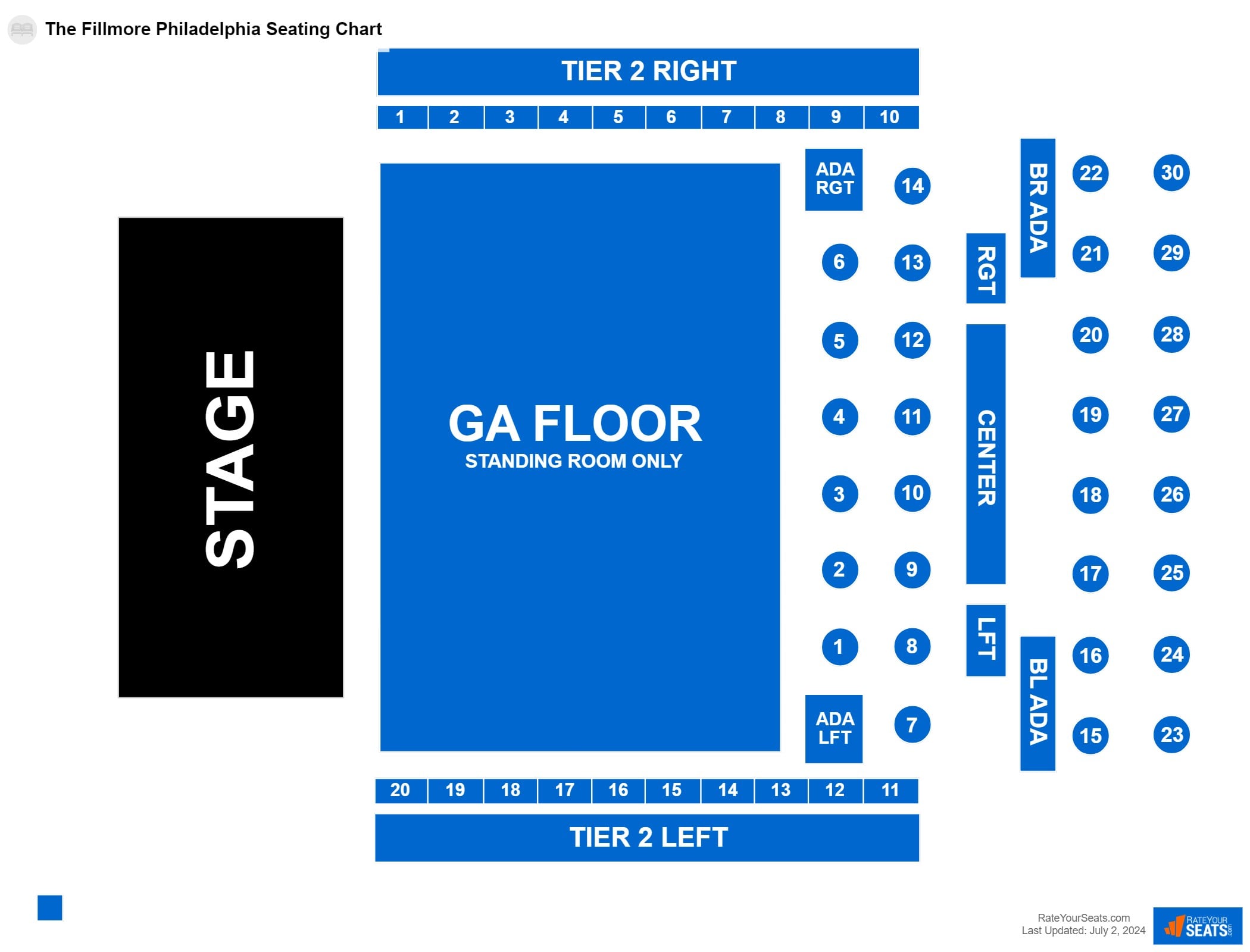
Fillmore Seating Chart Silver Spring - 2010) showed that high caffeine intake was associated with a non significant decrease of sperm concentration and total sperm count. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim). One notable study found that men who. Evidence from epidemiological studies on. High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. A recent study (jensen tk et al. Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen quality. Short answer caffeine and sperm: Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage. 2010) showed that high caffeine intake was associated with a non significant decrease of sperm concentration and total sperm count. Research published in human reproduction in 2018 demonstrated that men with high caffeine intake had an increased rate of dna fragmentation in their sperm. Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage. High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim). Evidence from epidemiological studies on. To summarize available evidence, we performed a systematic review of observational studies on the relation between coffee/caffeine intake and parameters of male fertility including sperm. A recent study (jensen tk et al. Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen quality. Research published in human reproduction in 2018 demonstrated that men with high caffeine intake had an increased rate of dna fragmentation in their sperm. Evidence from epidemiological studies on semen. One notable study found that men who. Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage.. Research published in human reproduction in 2018 demonstrated that men with high caffeine intake had an increased rate of dna fragmentation in their sperm. High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen. Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage. Short answer caffeine and sperm: Evidence from epidemiological studies on semen. Research published in human reproduction in 2018 demonstrated that men with high caffeine intake had an increased rate of dna fragmentation in their sperm. High caffeine. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim). 2010) showed that high caffeine intake was associated with a non significant decrease of sperm concentration and total sperm count. Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen quality. The literature suggests that. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. 2010) showed that high caffeine intake was associated with a non significant decrease of sperm concentration and total sperm count. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim). Studies have shown that. Evidence from epidemiological studies on semen. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage. A recent study (jensen tk et al. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake. Evidence from epidemiological studies on. Short answer caffeine and sperm: High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. To summarize available evidence, we performed a systematic review of observational studies on. 2010) showed that high caffeine intake was associated with a non significant decrease of sperm concentration and total sperm count. Short answer caffeine and sperm: Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage. A recent study (jensen tk et al. Evidence from epidemiological studies on. High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. Short answer caffeine and sperm: Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen quality. Studies. The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. Research published in human reproduction in 2018 demonstrated that men with high caffeine intake had an increased rate of dna fragmentation in their sperm. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim).. A recent study (jensen tk et al. One notable study found that men who. Short answer caffeine and sperm: The literature suggests that caffeine intake, possibly through sperm dna damage, may negatively affect male reproductive function. To summarize available evidence, we performed a systematic review of observational studies on the relation between coffee/caffeine intake and parameters of male fertility including sperm. High caffeine intake, especially from sugary sodas and energy drinks, may negatively affect sperm count, semen volume, and testicular function. Evidence from epidemiological studies on. Evidence from epidemiological studies on semen. Studies have shown that high caffeine intake could potentially impact sperm concentration and motility (how well sperm can swim). Studies have shown that excessive caffeine intake can reduce fertility in men by negatively impacting semen quality. Research suggests that high caffeine consumption is linked to dna damage, specifically aneuploidy and dna fragmentation, but not other markers of dna damage.The Fillmore Philadelphia Seating Chart
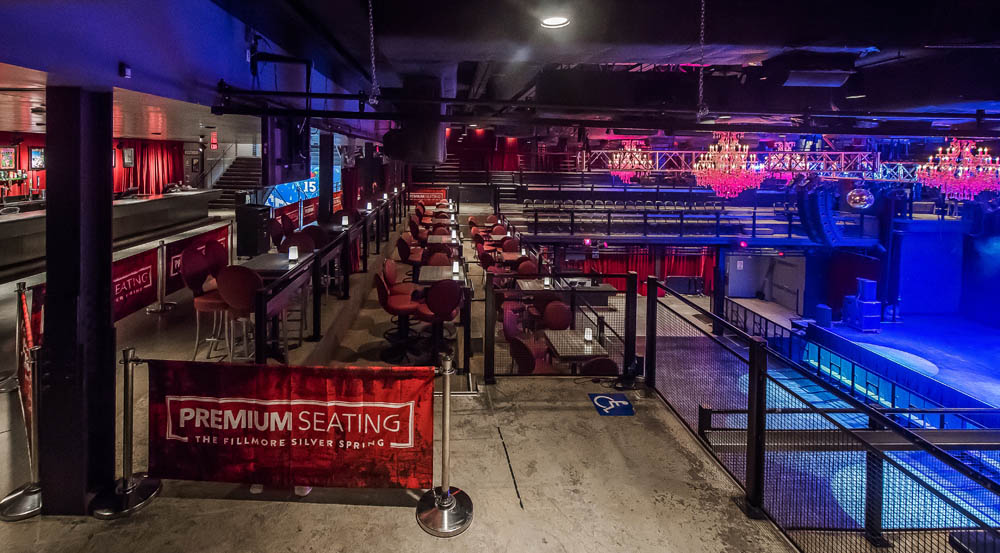
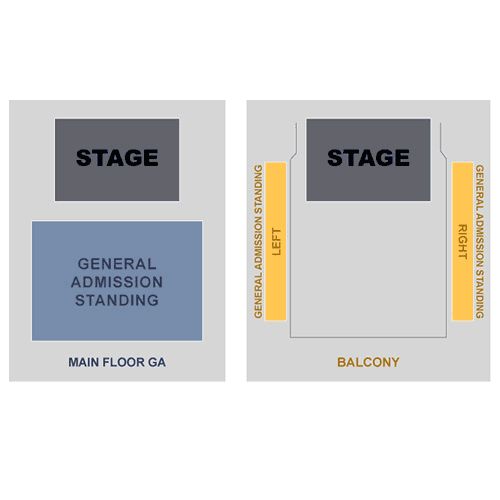
Fillmore Silver Spring Seating Chart
Fillmore Seating Chart Silver Spring Portal.posgradount.edu.pe
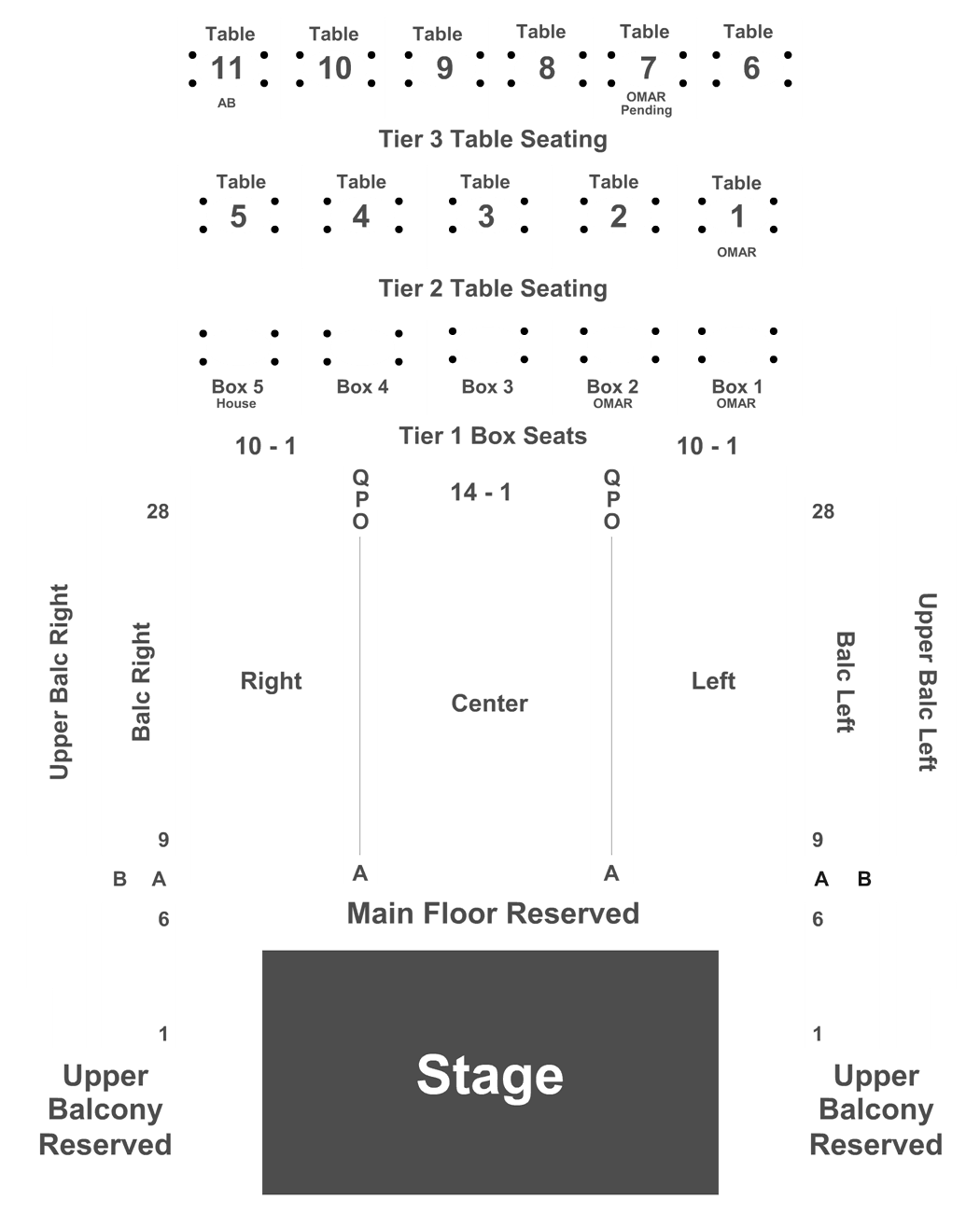
The Fillmore Silver Spring Md Seating Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
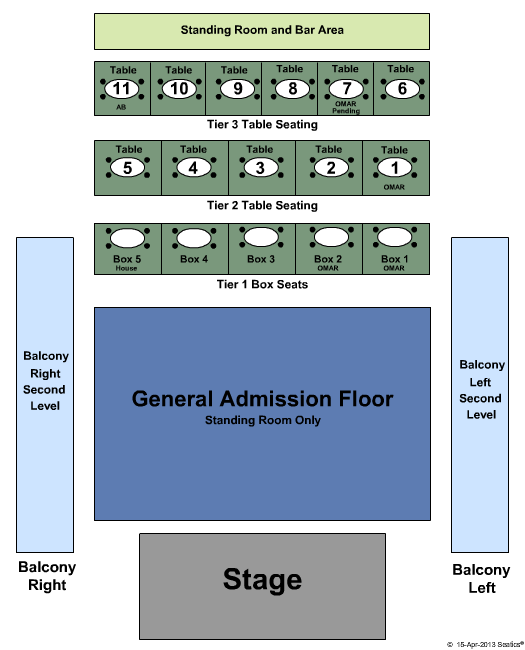
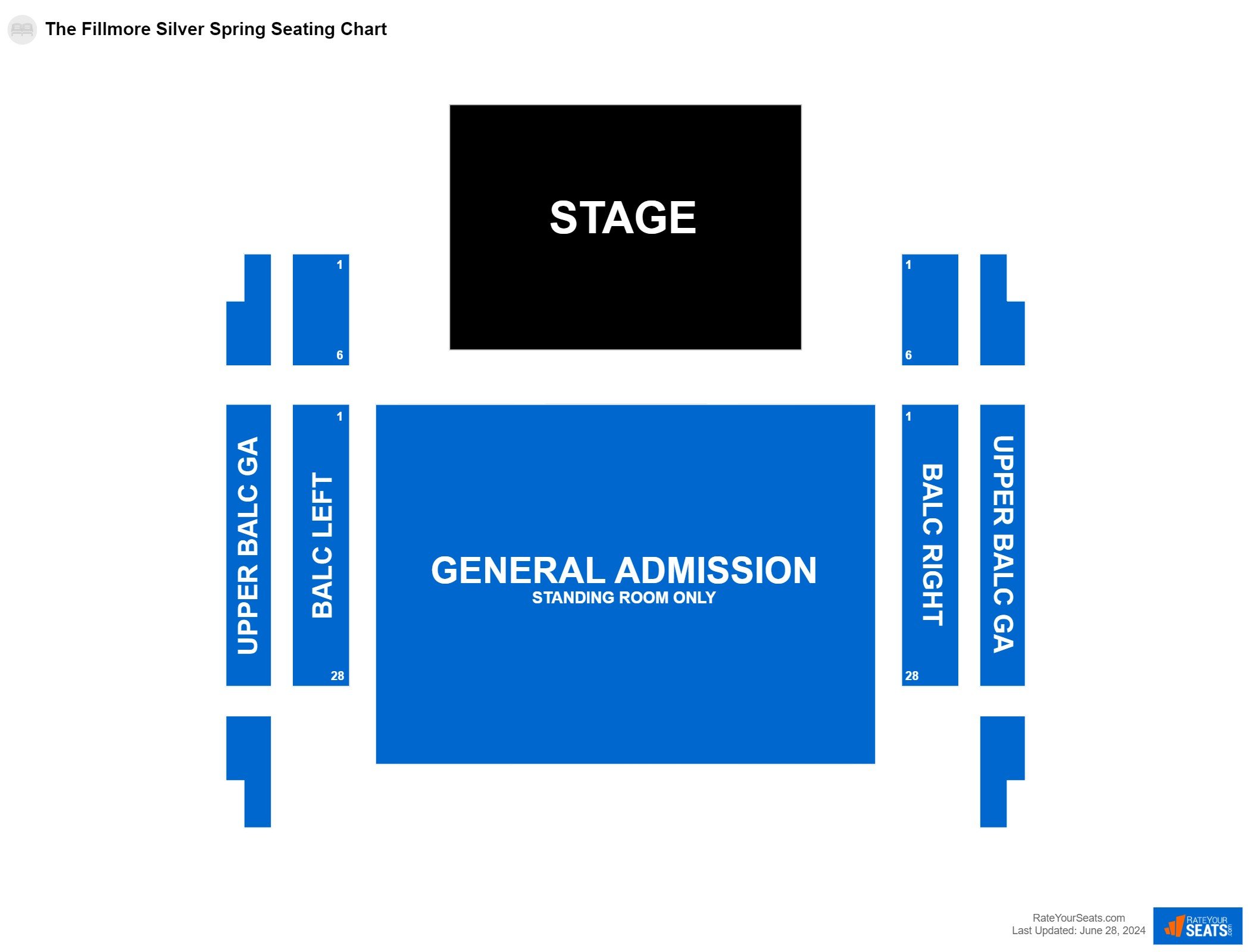
The Fillmore Silver Spring Seating Chart The Fillmore Silver Spring Event Tickets & Schedule
Fillmore Silver Spring
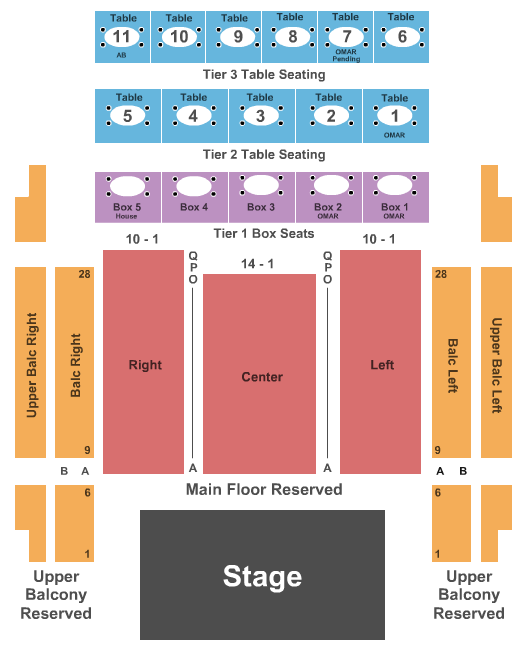
The Fillmore Silver Spring Md Seating Chart Ponasa
The Fillmore Silver Spring Md Seating Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
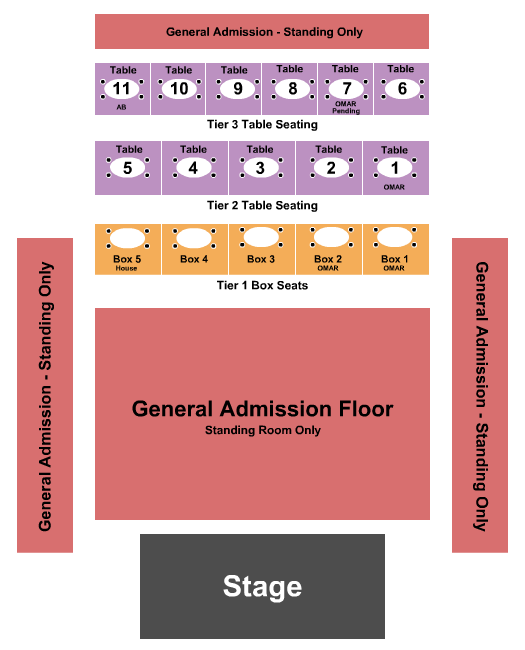
Silver Spring Fillmore Seating Chart
The Fillmore Silver Spring Seating Chart
Research Published In Human Reproduction In 2018 Demonstrated That Men With High Caffeine Intake Had An Increased Rate Of Dna Fragmentation In Their Sperm.
The Literature Suggests That Caffeine Intake, Possibly Through Sperm Dna Damage, May Negatively Affect Male Reproductive Function.
2010) Showed That High Caffeine Intake Was Associated With A Non Significant Decrease Of Sperm Concentration And Total Sperm Count.
Related Post: