Fermentation Chart
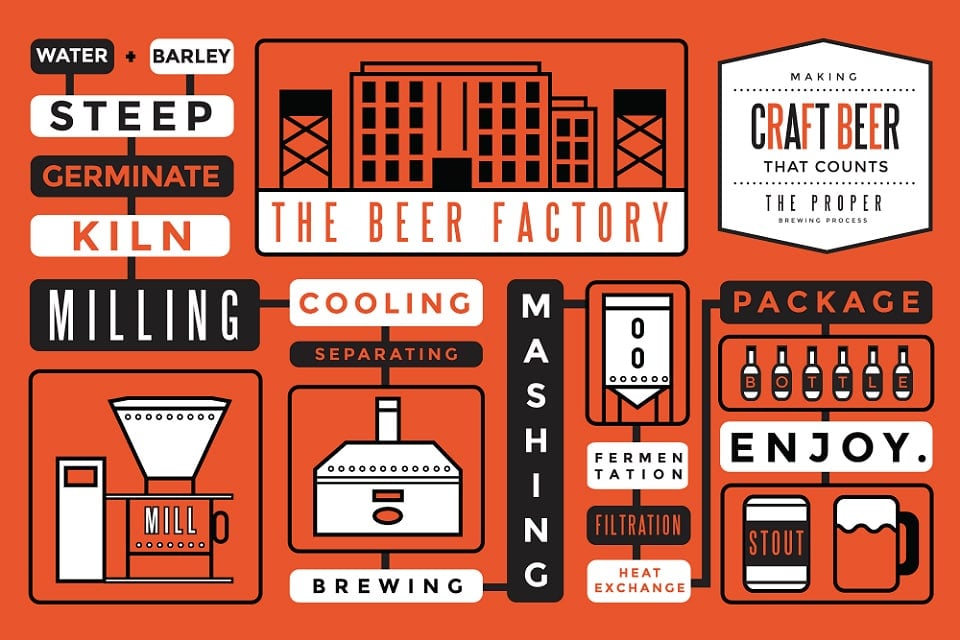
Fermentation Chart - Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. Fermentation is a metabolic process in organisms that converts carbohydrates into chemical energy, without requiring oxygen. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. Fermentation, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. Fermentation is defined as a process in which chemical changes occur in an organic substrate through the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms. Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds to produce substances that can be used in making chemical energy. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. In other words, it is an anaerobic process. Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process in which organic substrates are converted into simpler compounds, producing energy, primarily atp, without the use of. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Fermentation, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. Fermentation is defined as a process in which chemical changes occur in an organic substrate through the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms. Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds to produce substances that can be used in making chemical energy. More broadly, fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the production of. Understanding the fermentation process and. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. This process occurs in an. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. Fermentation is defined as a process in which chemical changes occur in an organic substrate through the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms. Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds to produce. Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process in which organic substrates are converted into simpler compounds, producing energy, primarily atp, without the use of. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds. This process occurs in an. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Fermentation is a metabolic process in organisms that converts carbohydrates into chemical energy, without requiring oxygen. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. In other words, it is an anaerobic process. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. Fermentation is defined as a process in which chemical changes occur. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process in which organic substrates are converted into simpler compounds, producing energy, primarily atp, without the use of. Fermentation, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. This process occurs. Understanding the fermentation process and. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like yeast and bacteria convert sugars into alcohol, gases, or acids. Fermentation is a metabolic process in organisms that converts carbohydrates into chemical energy, without requiring oxygen. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. This process. Fermentation, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Understanding the fermentation process and. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen.. Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (atp) and organic end products. In other words, it is an anaerobic process. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. Fermentation is a metabolic process in organisms. This process occurs in an. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. More broadly, fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the production of. Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds to produce substances that can be used in making chemical energy. Fermentation. Fermentation is a biochemical process in which carbohydrates like glucose or starch are converted to alcohol or acid without oxygen. This process occurs in an. In other words, it is an anaerobic process. Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds to produce substances that can be used in making chemical energy. Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeasts, or molds convert carbohydrates (like sugars and starches) into alcohol or acids. Understanding the fermentation process and. Fermentation is defined as a process in which chemical changes occur in an organic substrate through the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms. Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process in which organic substrates are converted into simpler compounds, producing energy, primarily atp, without the use of. Fermentation is a metabolic process in which microorganisms like yeasts, bacteria, and molds convert organic compounds (such as carbohydrates) into simpler. Fermentation is a metabolic process in organisms that converts carbohydrates into chemical energy, without requiring oxygen. More broadly, fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the production of.The Beer Factory Fermentation Chart GearMoose
Mastering Fermentation Fermentation Process
Brine chart for fermentation Pickling recipes, Brine recipe, Fermented foods
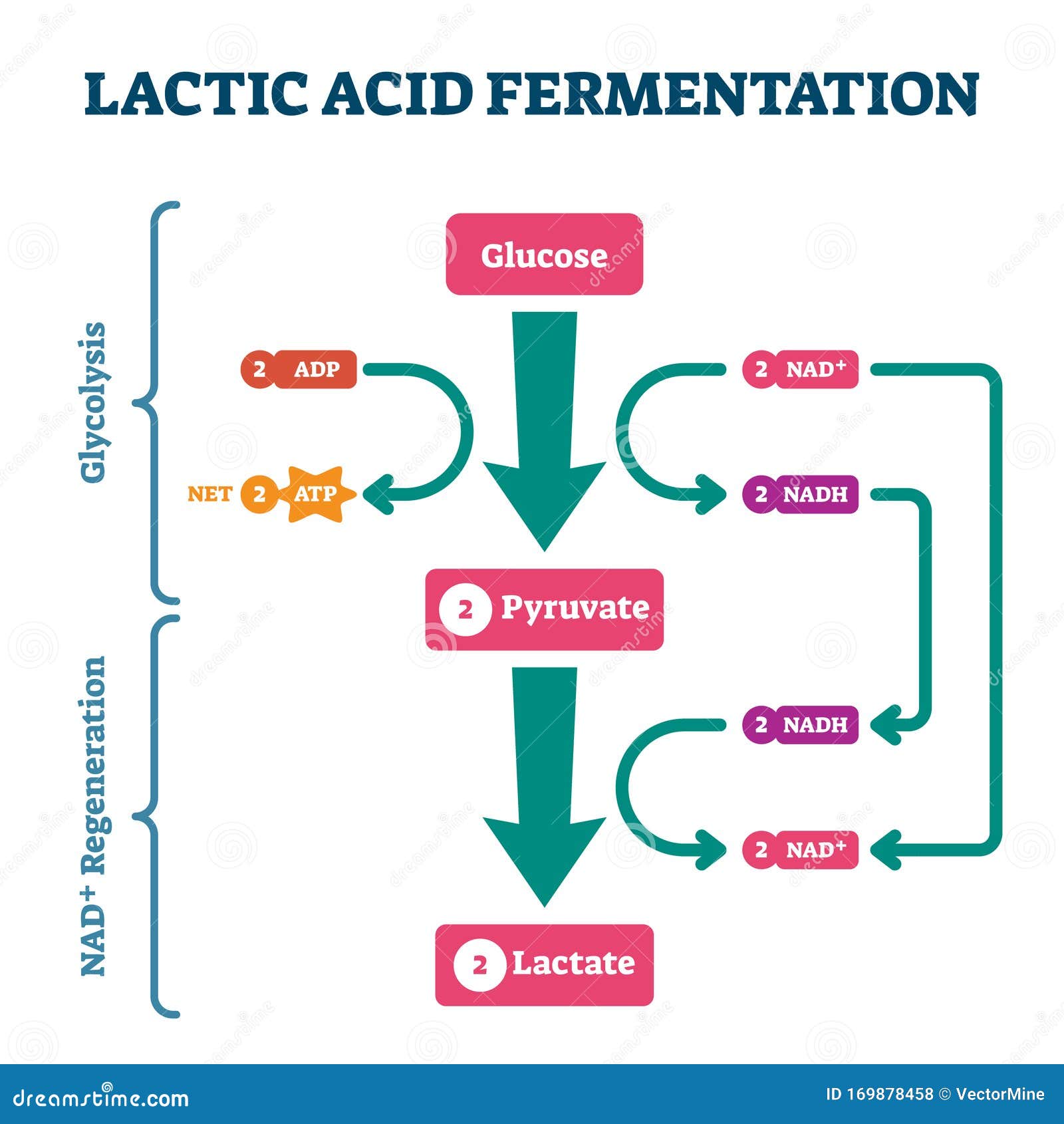
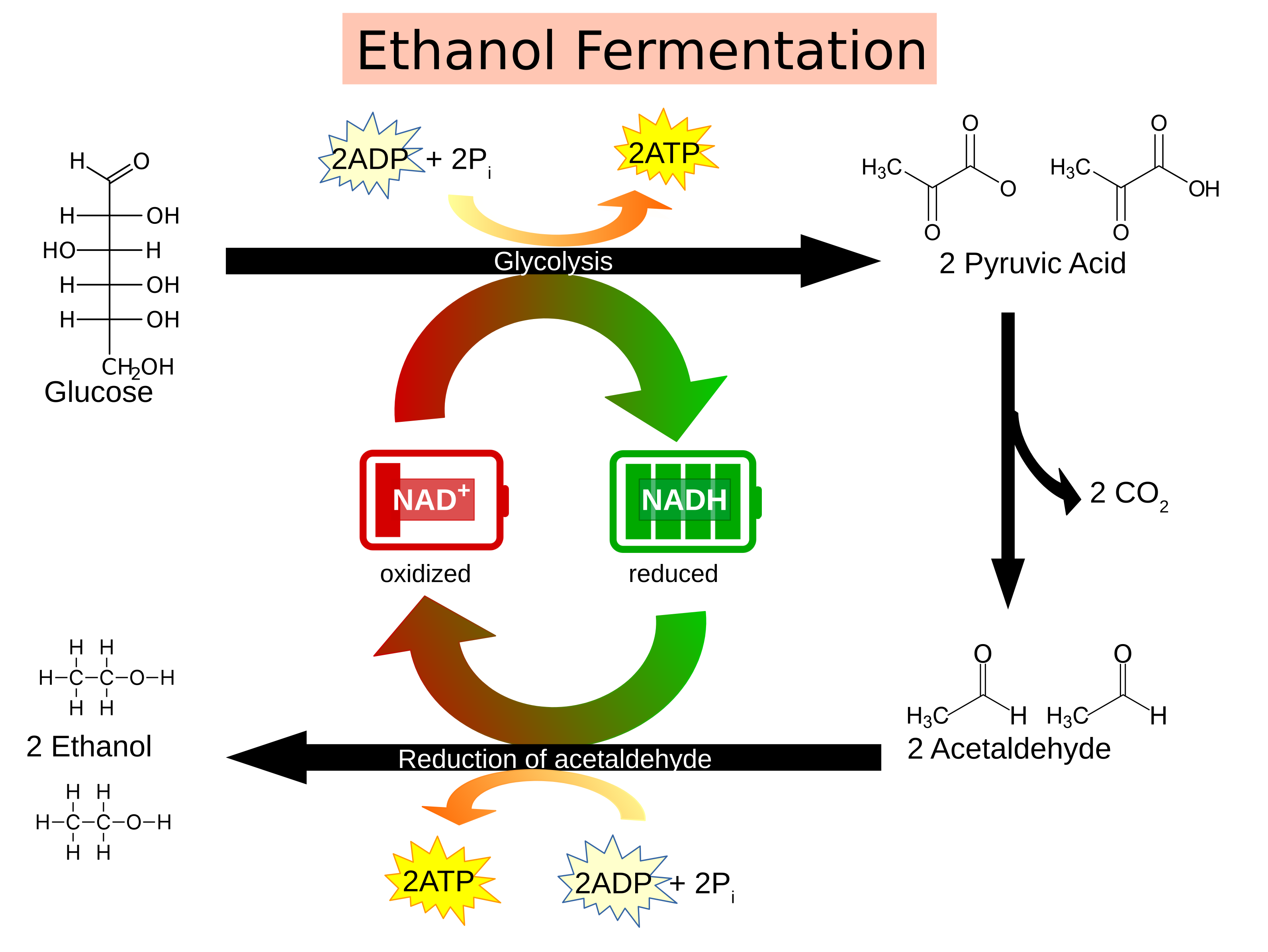
Fermentation Process Diagram
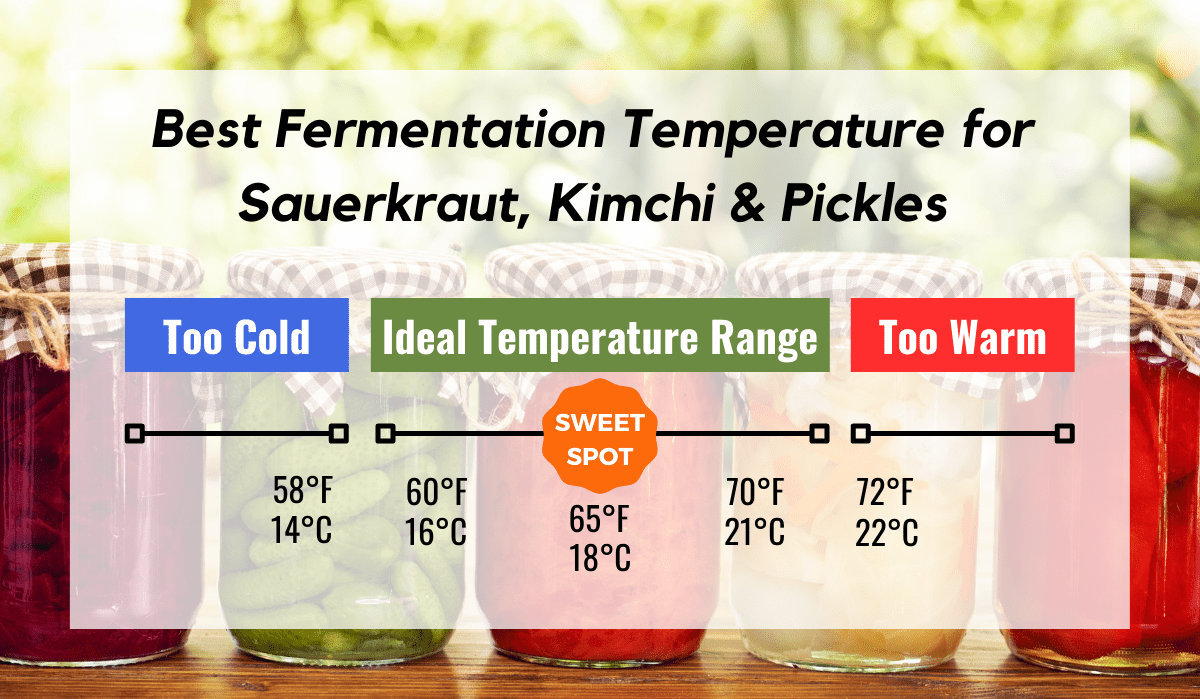
The Best Fermentation Temperature {Sauerkraut, Pickles, Kimchi}
Fermentation Diagram Labeled
Fermentation Periods (2008) Behance
Fermentation Chart Fermentation, Jar labels, Salt brine
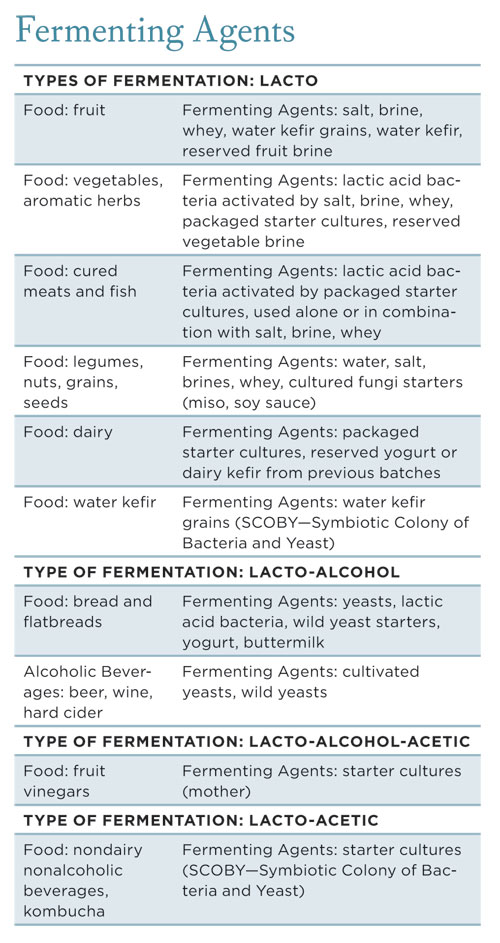
Infographic Agents of Fermentation
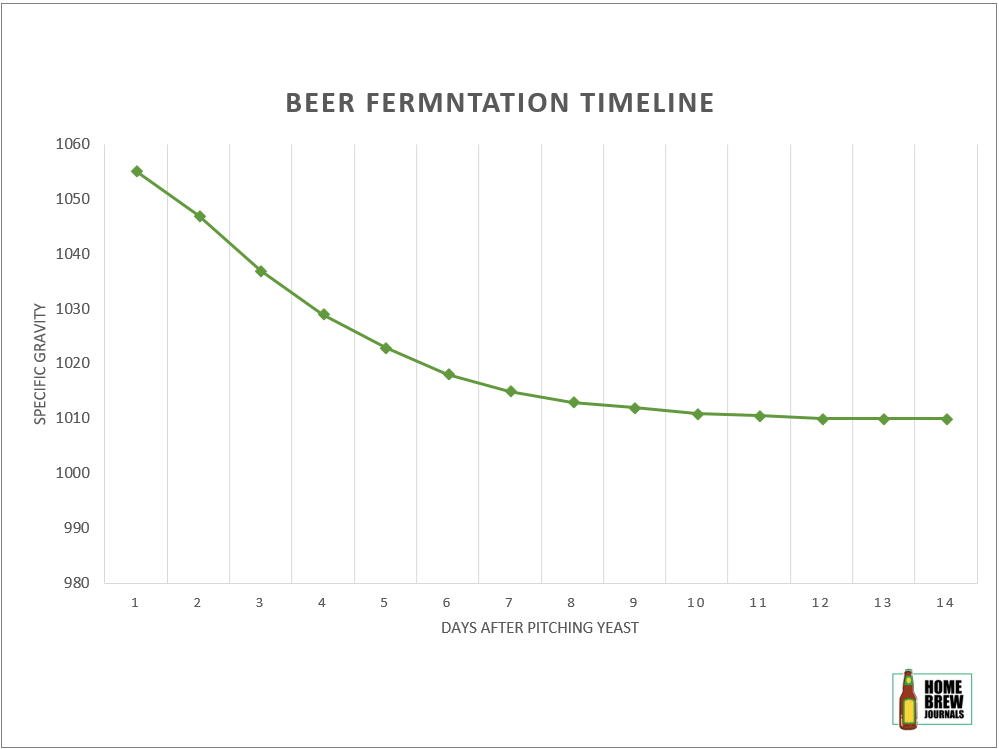
How long do you brew beer? (Beer fermentation time chart) Homebrew Journals
Fermentation, Chemical Process By Which Molecules Such As Glucose Are Broken Down Anaerobically.
Fermentation Is A Metabolic Process Where Microorganisms Like Yeast And Bacteria Convert Sugars Into Alcohol, Gases, Or Acids.
Fermentation Is A Type Of Anaerobic Metabolism Which Harnesses The Redox Potential Of The Reactants To Make Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp) And Organic End Products.
Related Post: