Excel Chart Logarithmic Scale
Excel Chart Logarithmic Scale - In most of the online resource i can find usually show me how to retrieve this information in vba. As far as i can tell, excel xp (which is what we're using). Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? It would mean you can apply textual functions like left/right/mid on a conditional basis without. Is there any direct way to get this information in a cell? In your example you fix the. =sum(!b1:!k1) when defining a name for a cell and this was entered into the refers to field. In the popup window, you can also select always use this cell as a parameter. In a text about excel i have read the following: Excel has recently introduced a huge feature called dynamic arrays. To solve this problem in excel, usually i would just type in the literal row number of the cell above, e.g., if i'm typing in cell a7, i would use the formula =a6. That will popup a small window asking for the cell/data/etc when you go back to excel. As far as i can tell, excel xp (which is what we're using). Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? Is there any direct way to get this information in a cell? Excel has recently introduced a huge feature called dynamic arrays. Not the last character/string of the string, but the position of a. I need to parse an iso8601 date/time format with an included timezone (from an external source) in excel/vba, to a normal excel date. In most of the online resource i can find usually show me how to retrieve this information in vba. In your example you fix the. To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. In a text about excel i have read the following: In the popup window, you can also select always use this cell as a parameter. Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? Boolean values true and false in. In your example you fix the. Excel has recently introduced a huge feature called dynamic arrays. In the popup window, you can also select always use this cell as a parameter. Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. I need to parse an iso8601 date/time format with an included timezone (from an external source) in excel/vba, to a normal excel date. In a text about excel i have read the following: Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? And along with that, excel also started to make a. It would mean you can apply textual functions like left/right/mid on a conditional basis without. To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. In your example you fix the. Not the last character/string of the string, but the position of a. I need to parse an iso8601 date/time format with an included timezone (from an external. Excel has recently introduced a huge feature called dynamic arrays. To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. Boolean values true and false in excel are treated as 1 and 0, but we need to convert them. =sum(!b1:!k1) when defining a name for a cell and this was entered into the refers to field. Is there. And along with that, excel also started to make a substantial upgrade to their formula language. It would mean you can apply textual functions like left/right/mid on a conditional basis without. That will popup a small window asking for the cell/data/etc when you go back to excel. =sum(!b1:!k1) when defining a name for a cell and this was entered into. As far as i can tell, excel xp (which is what we're using). It would mean you can apply textual functions like left/right/mid on a conditional basis without. Not the last character/string of the string, but the position of a. In a text about excel i have read the following: Boolean values true and false in excel are treated as. Then if i copied that. In most of the online resource i can find usually show me how to retrieve this information in vba. The dollar sign allows you to fix either the row, the column or both on any cell reference, by preceding the column or row with the dollar sign. Boolean values true and false in excel are. And along with that, excel also started to make a substantial upgrade to their formula language. To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. Not the last character/string of the string, but the position of a. In your example you fix the. Then if i copied that. In your example you fix the. I need to parse an iso8601 date/time format with an included timezone (from an external source) in excel/vba, to a normal excel date. The dollar sign allows you to fix either the row, the column or both on any cell reference, by preceding the column or row with the dollar sign. Not the last. Is there any direct way to get this information in a cell? In most of the online resource i can find usually show me how to retrieve this information in vba. As far as i can tell, excel xp (which is what we're using). It would mean you can apply textual functions like left/right/mid on a conditional basis without. Is there an efficient way to identify the last character/string match in a string using base functions? Boolean values true and false in excel are treated as 1 and 0, but we need to convert them. In a text about excel i have read the following: I need to parse an iso8601 date/time format with an included timezone (from an external source) in excel/vba, to a normal excel date. Then if i copied that. To solve this problem in excel, usually i would just type in the literal row number of the cell above, e.g., if i'm typing in cell a7, i would use the formula =a6. To convert them into numbers 1 or 0, do some mathematical operation. In the popup window, you can also select always use this cell as a parameter. =sum(!b1:!k1) when defining a name for a cell and this was entered into the refers to field. Not the last character/string of the string, but the position of a. Excel has recently introduced a huge feature called dynamic arrays.How and Why you should use a Logarithmic Scale in an Excel Diagram
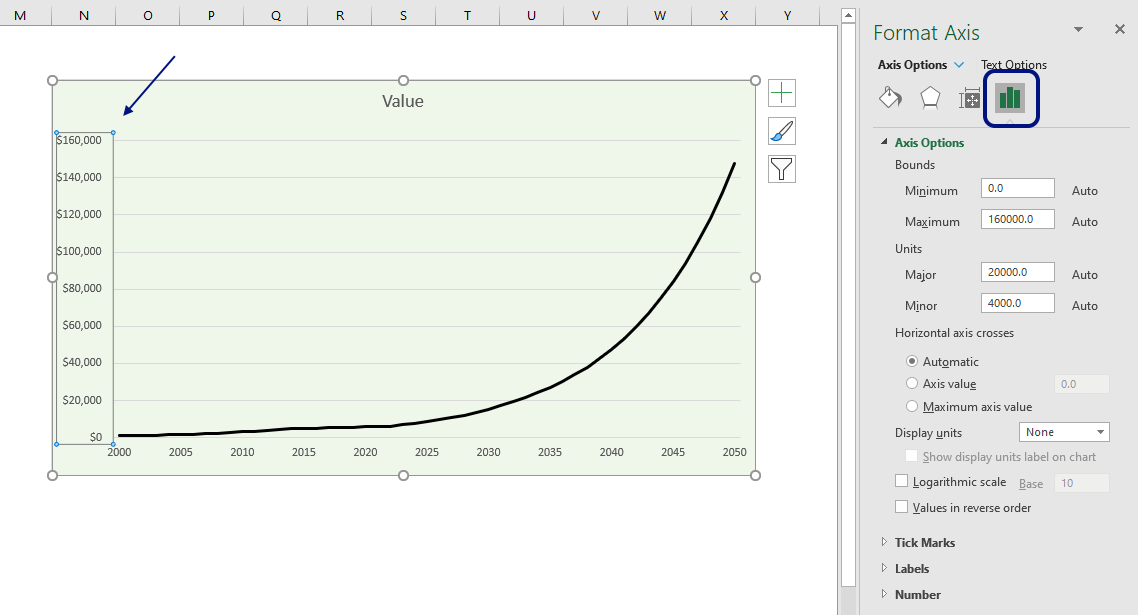
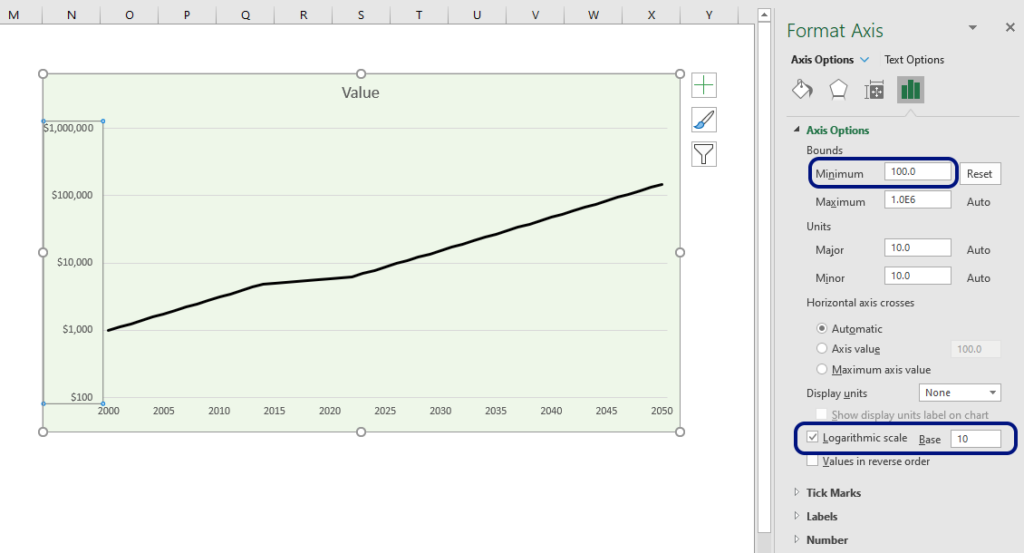
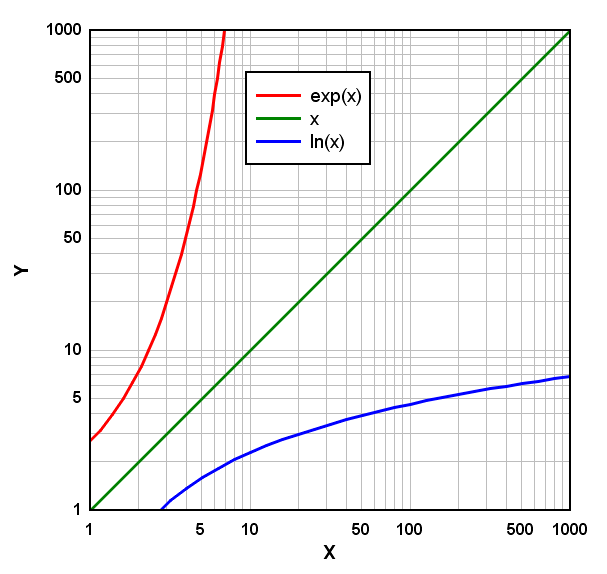
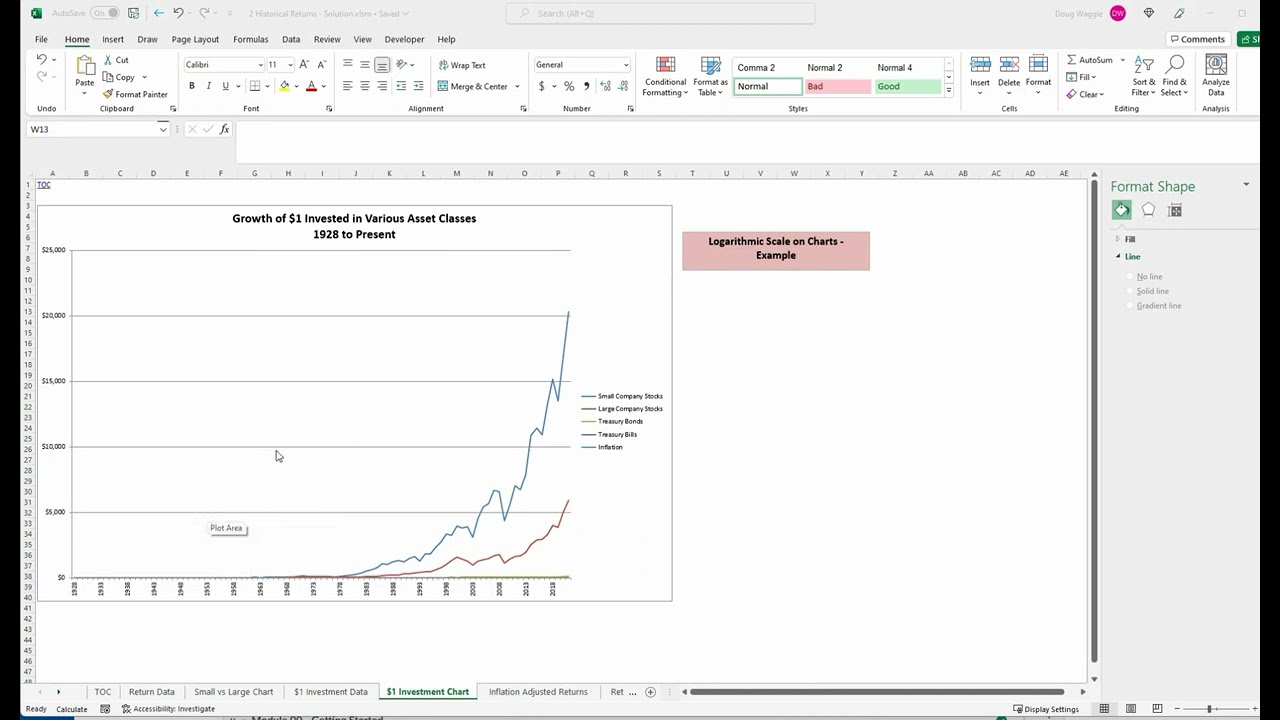
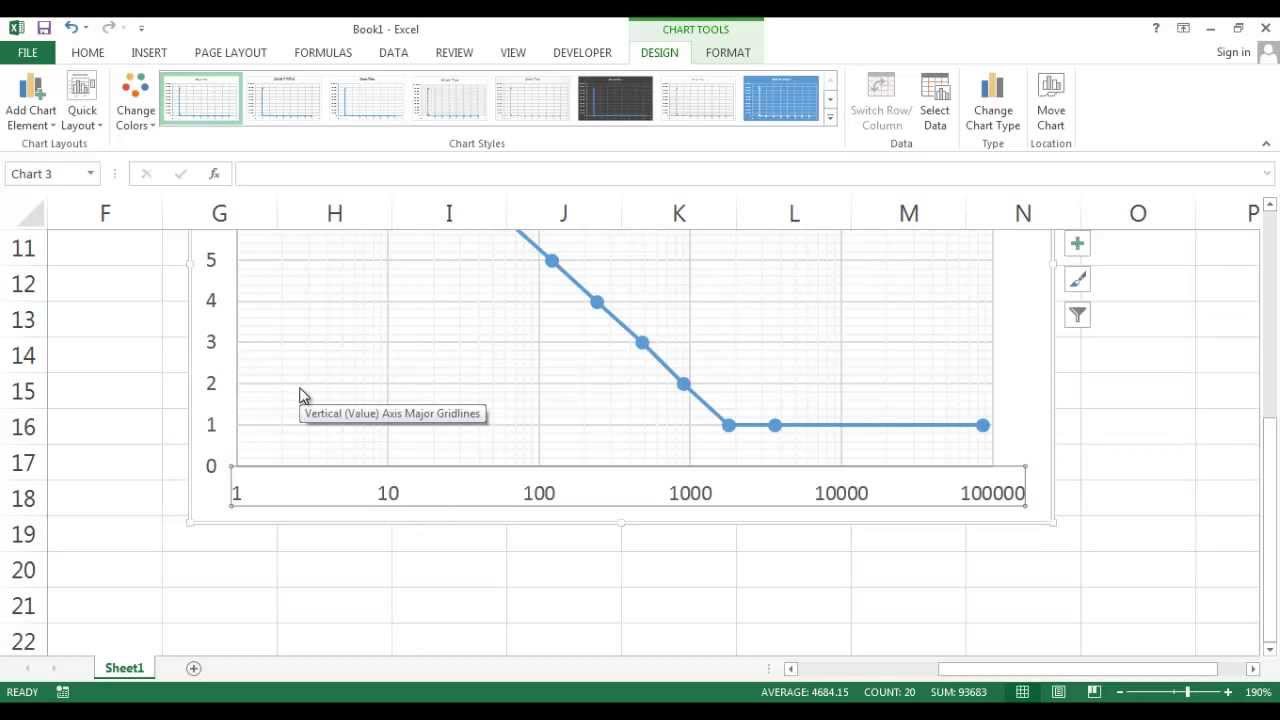
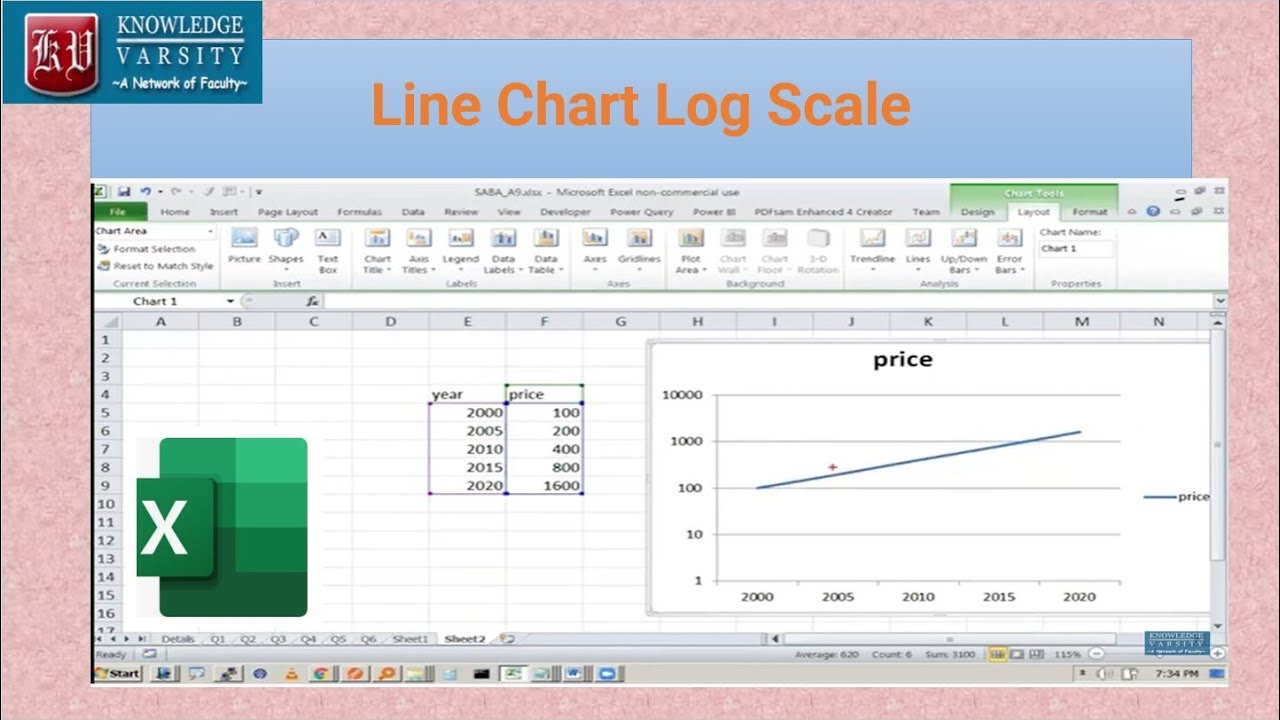
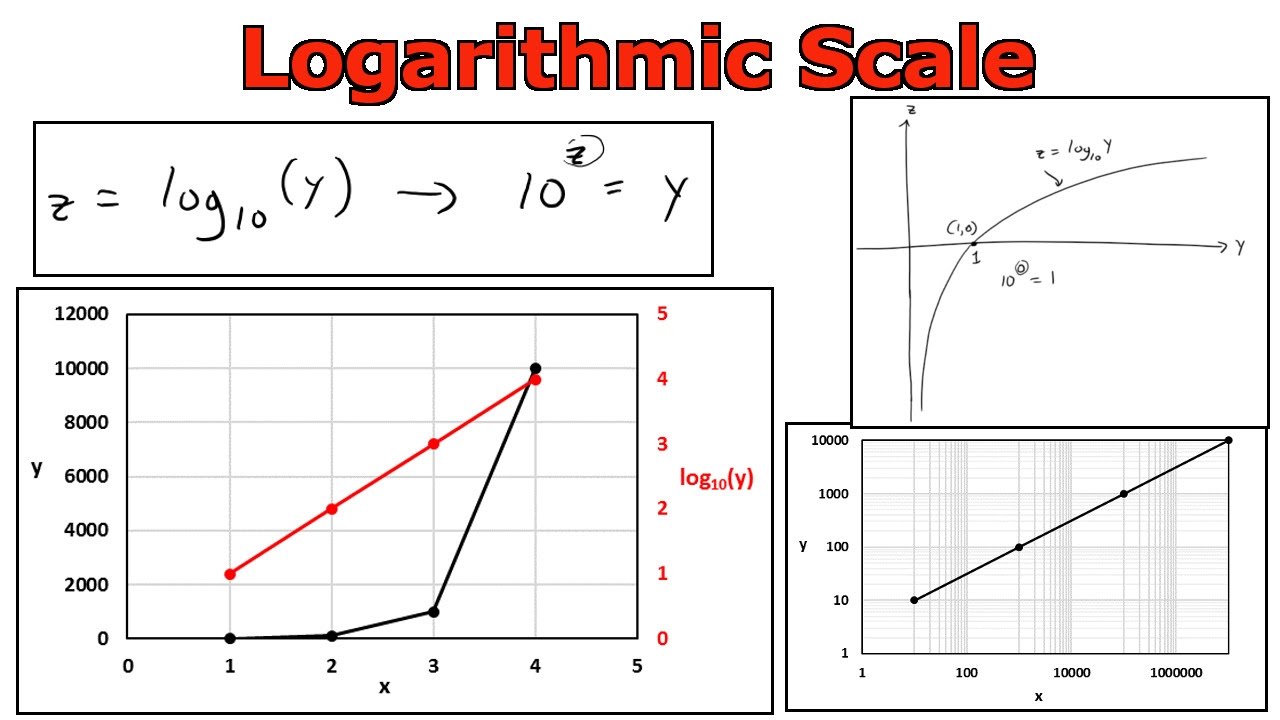
How and Why you should use a Logarithmic Scale in an Excel Diagram
excel log scale chart Graph logarithmic paper chart template values table exceltemplate spreadsheet
Change Y Axis to Logarithmic Scale in Microsoft Excel With One Click! tutorial howto trending
Excel Show Logarithmic Scale on Chart YouTube
How to Draw Logarithmic Graph in Excel 2013 YouTube
excel log scale chart Graph logarithmic paper chart template values table exceltemplate spreadsheet
Logarithmic Scale Graphing in Microsoft Excel YouTube
excel log scale chart Graph logarithmic paper chart template values table exceltemplate spreadsheet
Excel Chart Logarithmic Scale
That Will Popup A Small Window Asking For The Cell/Data/Etc When You Go Back To Excel.
In Your Example You Fix The.
And Along With That, Excel Also Started To Make A Substantial Upgrade To Their Formula Language.
The Dollar Sign Allows You To Fix Either The Row, The Column Or Both On Any Cell Reference, By Preceding The Column Or Row With The Dollar Sign.
Related Post: