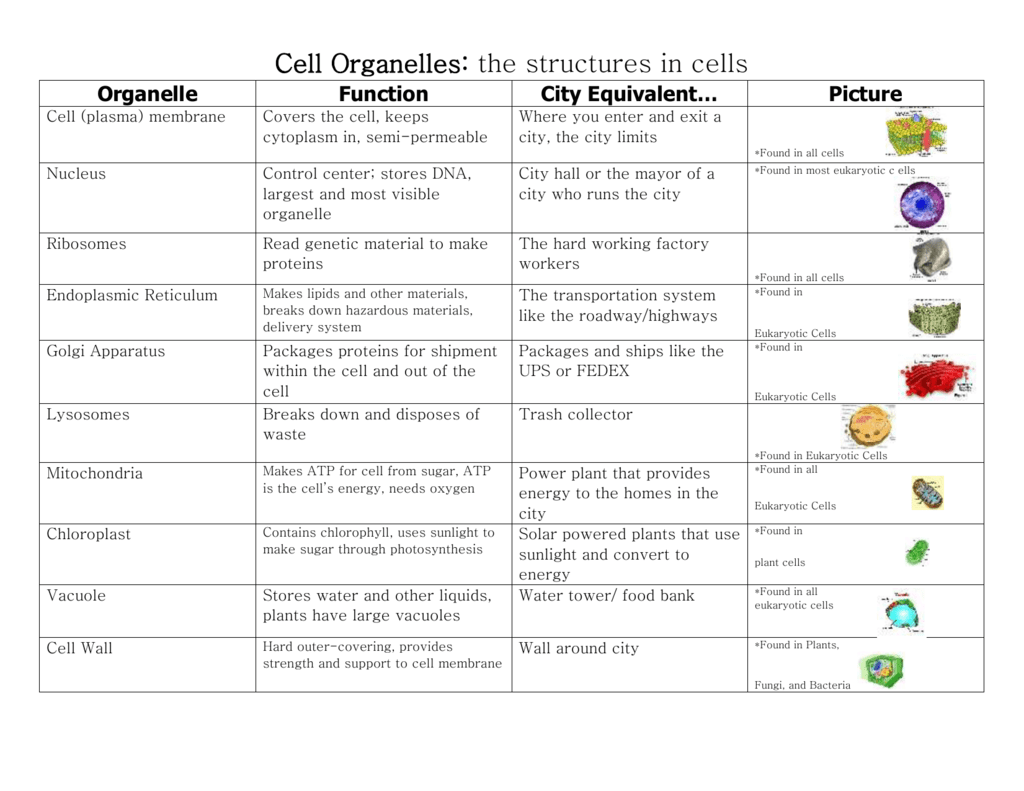
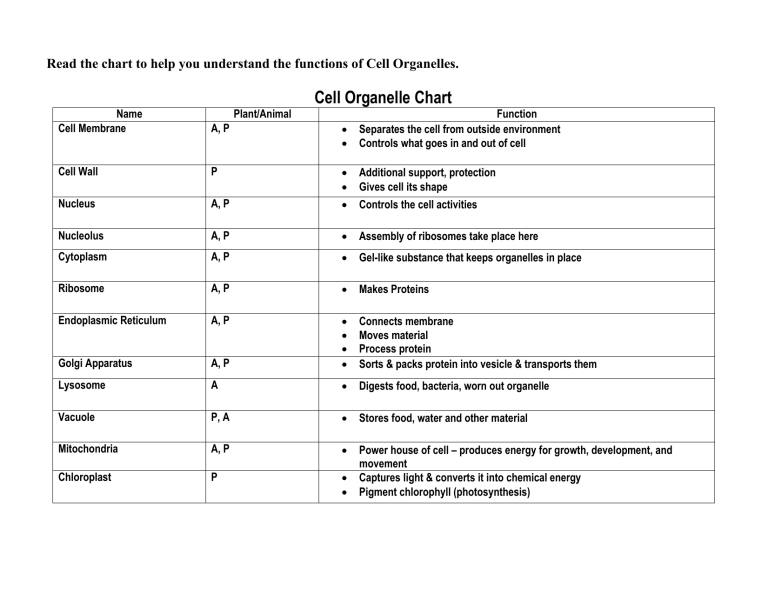
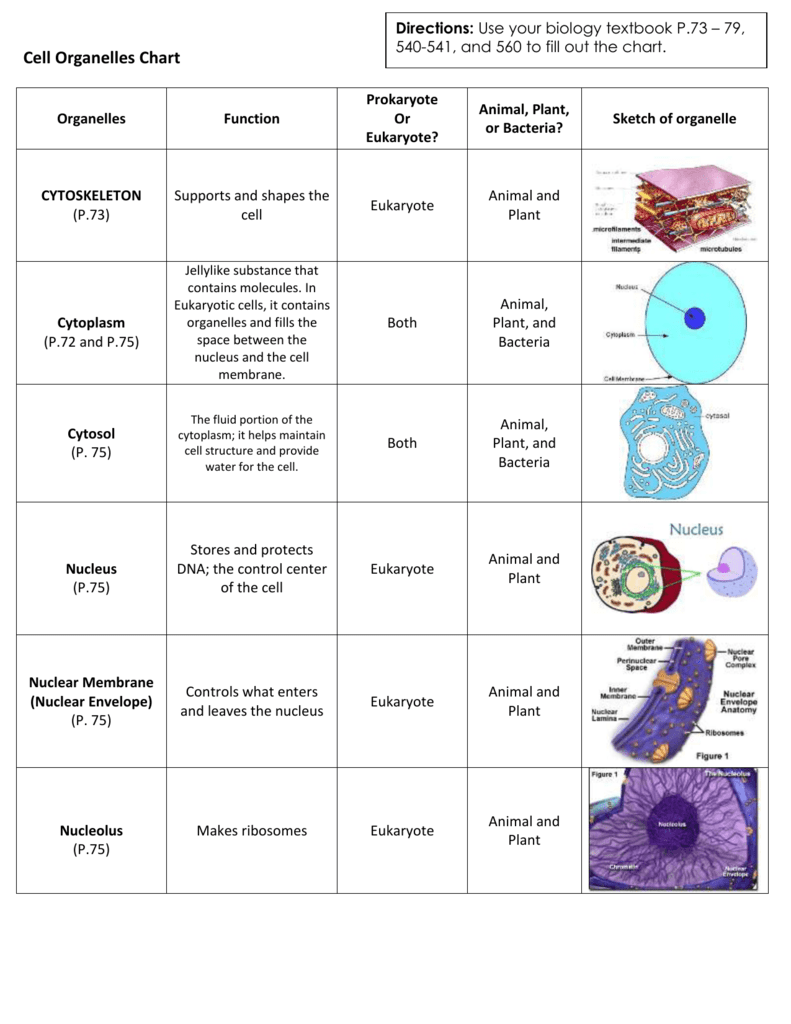
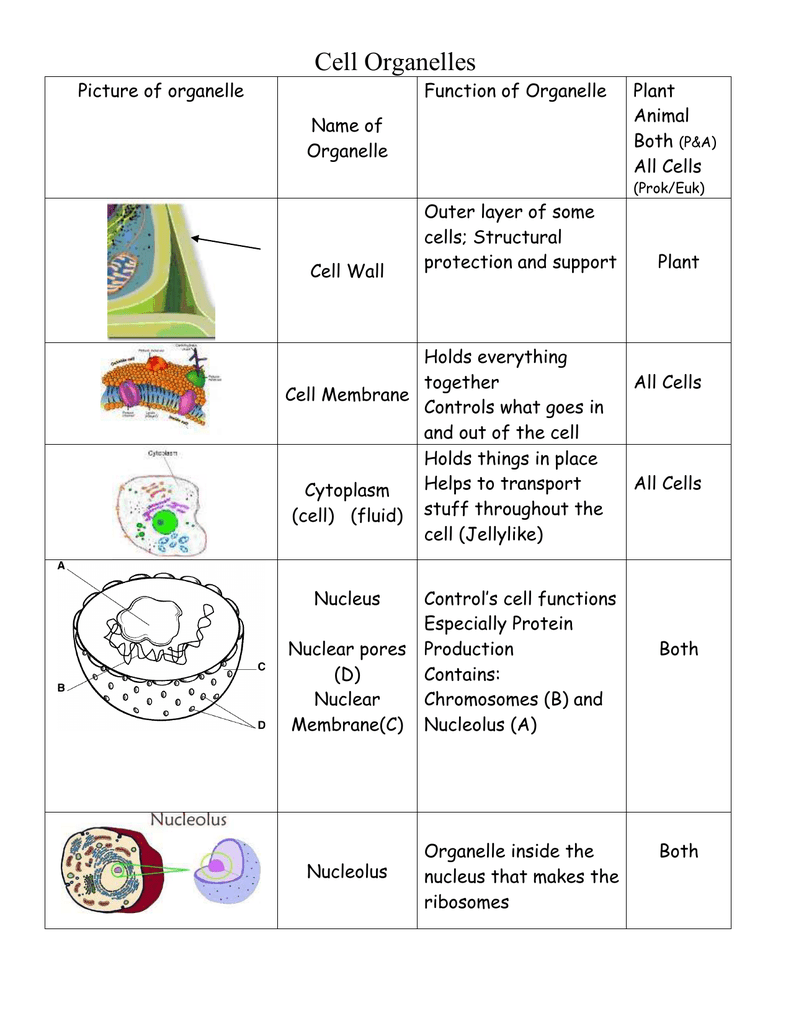
Cells And Organelles Chart
Cells And Organelles Chart - Cells are broadly categorized into two types: A single cell is often a complete. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Some organisms consist of only one cell, while others (like humans) have trillions of cells! They can range from the minuscule mycoplasmas, the smallest known cells, to complex multicellular organisms like. Each type has distinct characteristics and. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. All of them look quite different. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Cells are the structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Cells, the basic building blocks of all living organisms, can be broadly classified into two types: Each type has distinct characteristics and. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. All of them look quite different. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Cells are the microscopic units that make up humans and every other living organism. Each type has distinct characteristics and. Some organisms consist of only one cell, while others (like humans) have trillions of cells! The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. A single cell is often a complete. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. A single cell is often a complete. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Some organisms consist of only one cell, while others (like humans) have trillions of cells! Cells are the microscopic units that make up humans and every other living organism. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Each type has distinct characteristics and. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Some organisms consist of only one cell, while others (like humans) have trillions of cells! Cells are broadly categorized into two types: All of them look quite different. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Other organisms, such as humans, are multicellular,. Cells, the basic building blocks of all living organisms, can be broadly classified into two types: Cells are the structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. Cells are incredibly diverse in their morphology and function. Other organisms, such as humans, are multicellular,. A single cell is often a complete. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. And that’s due to the highly organized cells from which they’re made. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. All of them look quite different. Cells are the structural and functional unit of all living organisms. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. Cells, the basic building blocks of all living organisms, can be broadly classified into two types: Other organisms, such as humans, are multicellular,. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Cells, the basic building blocks of all living organisms, can be broadly classified into two types: Cells are broadly categorized into two types: They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. They can range from the minuscule mycoplasmas, the smallest known cells, to. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. Each type has distinct characteristics and. They can range from the minuscule mycoplasmas, the smallest known cells, to complex multicellular organisms like. Cells are incredibly diverse in their morphology and function. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: Cells are the microscopic units that make up humans and every other living organism. The human body has roughly 37 trillion cells. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Other organisms, such as humans, are multicellular,. A single cell is often a complete. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients. Some organisms consist of only one cell, while others (like humans) have trillions of cells! All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Cells emerged on earth about 4 billion years ago. Cells are the structural and functional unit of all living organisms.Animal Cell Structure And Functions Of Organelles / Animal Cell Structure, Function and Types
Cell Organelle — Types & Functions Expii
Unit 2 Cells & Organelles Mr Plowman
Cell Organelle Chart Functions & Types
Cell Organelles
Cell Organelle
Structure And Function Of Cytoplasmic Organelles Of Cell
Organelles And Functions Biology College Biology Clas vrogue.co
Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
Animal Cells Label The Organelles
And That’s Due To The Highly Organized Cells From Which They’re Made.
Cells, The Basic Building Blocks Of All Living Organisms, Can Be Broadly Classified Into Two Types:
The Human Body Is Composed Of Trillions Of Cells.
All Of Them Look Quite Different.
Related Post: