Alkalinity Chart
Alkalinity Chart - This is also called buffering capacity. If any changes are made to the water that could raise or lower the ph value, alkalinity acts as a buffer, protecting the. The alkalinity of water is a measure of how much acid it can neutralize. In this article, we will explore the definition of alkalinity, its chemical. Alkalinity is a measure of water’s ability to resist ph changes that lead to acidity, or to neutralize acids, and maintain a fairly stable ph. Alkalinity is caused by strong bases and the salts of. Alkalinity measures water’s ability to maintain a stable ph level. The higher the alkalinity of a water body, the better it can protect itself against the. In the world of water chemistry, alkalinity often plays a crucial, yet somewhat unnoticed, role. It is measured by titrating the solution with an acid such as hcl until its ph changes abruptly, or. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer solution composed of weak acids and their conjugate bases. The alkalinity of water is a measure of how much acid it can neutralize. It is measured by titrating the solution with an acid such as hcl until its ph changes abruptly, or. It’s not a specific molecule but rather a measure of a water body’s ability to neutralize acids and. If any changes are made to the water that could raise or lower the ph value, alkalinity acts as a buffer, protecting the. Alkalinity is a measure of water’s ability to resist ph changes that lead to acidity, or to neutralize acids, and maintain a fairly stable ph. In the world of water chemistry, alkalinity often plays a crucial, yet somewhat unnoticed, role. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. Alkalinity is caused by strong bases and the salts of. Total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water that can both attract and release hydrogen ions (h +). In this article, we will explore the definition of alkalinity, its chemical. It’s not a specific molecule but rather a measure of a water body’s ability to neutralize acids and. It is measured by titrating the solution with an acid such as hcl until its ph changes abruptly, or. If any changes are made to the water that could raise. Total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water that can both attract and release hydrogen ions (h +). If any changes are made to the water that could raise or lower the ph value, alkalinity acts as a buffer, protecting the. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide,. Alkalinity is a measure of water’s ability to resist ph changes that lead to acidity, or to neutralize acids, and maintain a fairly stable ph. In this article, we will explore the definition of alkalinity, its chemical. The higher the alkalinity of a water body, the better it can protect itself against the. Unlike ph, which measures acidity or alkalinity,. In this article, we will explore the definition of alkalinity, its chemical. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. This ability is usually referred to as water’s “buffering. This is also called buffering capacity. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer. This is also called buffering capacity. Unlike ph, which measures acidity or alkalinity, alkalinity quantifies water's buffering capacity. If any changes are made to the water that could raise or lower the ph value, alkalinity acts as a buffer, protecting the. In the world of water chemistry, alkalinity often plays a crucial, yet somewhat unnoticed, role. Alkalinity is produced by. This ability is usually referred to as water’s “buffering. Alkalinity measures water’s ability to maintain a stable ph level. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. It is measured by titrating the solution with an acid such as hcl until its. This is also called buffering capacity. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. Alkalinity is caused by strong bases and the salts of. Alkalinity is produced by substances that yield hydroxyl ions or by definition, a substance is alkaline if it. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. Unlike ph, which measures acidity or alkalinity, alkalinity quantifies water's buffering capacity. Total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water that can both attract and release. The higher the alkalinity of a water body, the better it can protect itself against the. This is also called buffering capacity. Total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water that can both attract and release hydrogen ions (h +). Unlike ph, which measures acidity or alkalinity, alkalinity quantifies water's buffering capacity.. It’s not a specific molecule but rather a measure of a water body’s ability to neutralize acids and. Alkalinity measures water’s ability to maintain a stable ph level. It is measured by titrating the solution with an acid such as hcl until its ph changes abruptly, or. Alkalinity is a measure of water’s ability to resist ph changes that lead. Alkalinity is the strength of a buffer solution composed of weak acids and their conjugate bases. The alkalinity of water is a measure of how much acid it can neutralize. Alkalinity is caused by strong bases and the salts of. Alkalinity refers to the quantitative measurement of the bicarbonate, carbonate, hydroxide, and hydrogen ions in a solution, expressed in equivalents per liter or milliequivalents per liter. Alkalinity is a measure of water’s ability to resist ph changes that lead to acidity, or to neutralize acids, and maintain a fairly stable ph. Alkalinity measures water’s ability to maintain a stable ph level. Alkalinity is produced by substances that yield hydroxyl ions or by definition, a substance is alkaline if it will neutralize hydrogen ions. In this article, we will explore the definition of alkalinity, its chemical. It’s not a specific molecule but rather a measure of a water body’s ability to neutralize acids and. In the world of water chemistry, alkalinity often plays a crucial, yet somewhat unnoticed, role. This is also called buffering capacity. Unlike ph, which measures acidity or alkalinity, alkalinity quantifies water's buffering capacity. The higher the alkalinity of a water body, the better it can protect itself against the.What Is The Ph Of Alkaline Water at Sarah Bruce blog
PH Alkalinity Mixing With Reaction Times Dynamix Agitators
What is Alkalinity?
Total Alkalinity PH, And Their Roles In Water Chemistry, 51 OFF
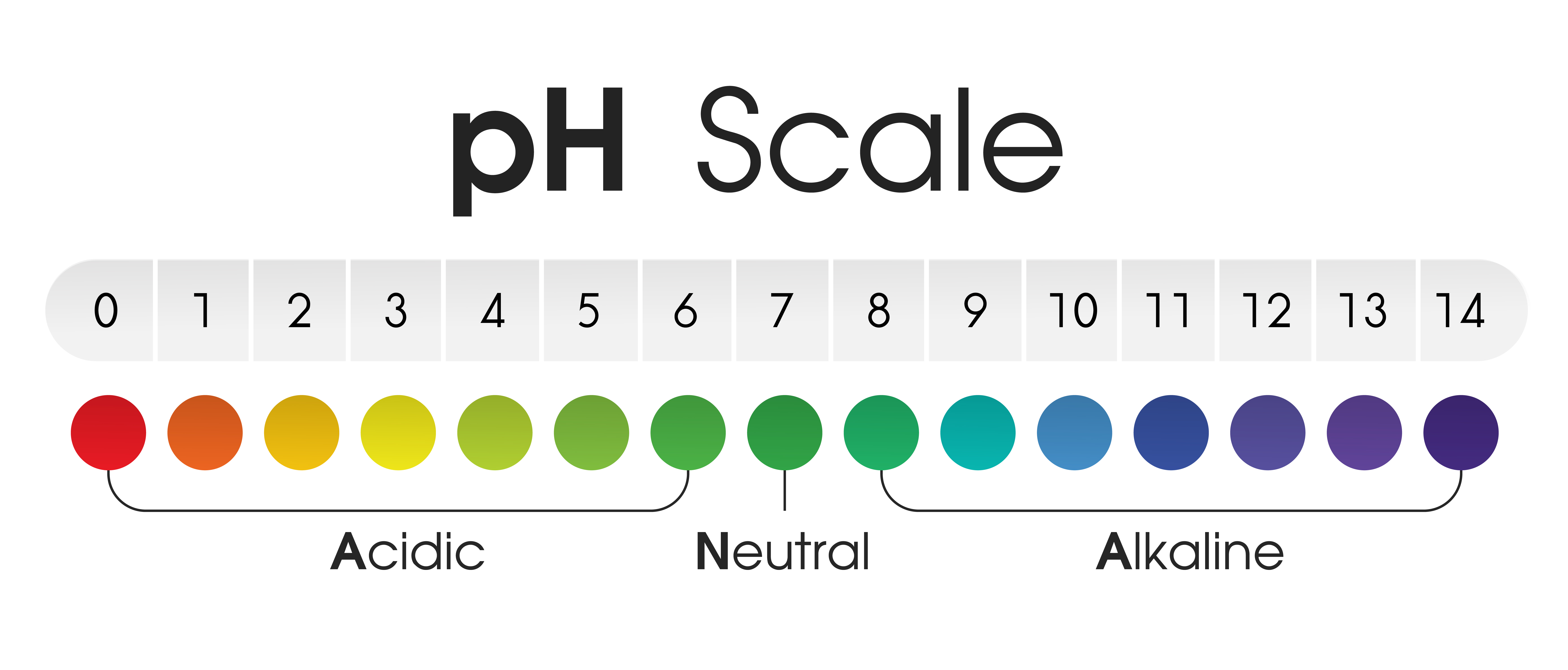
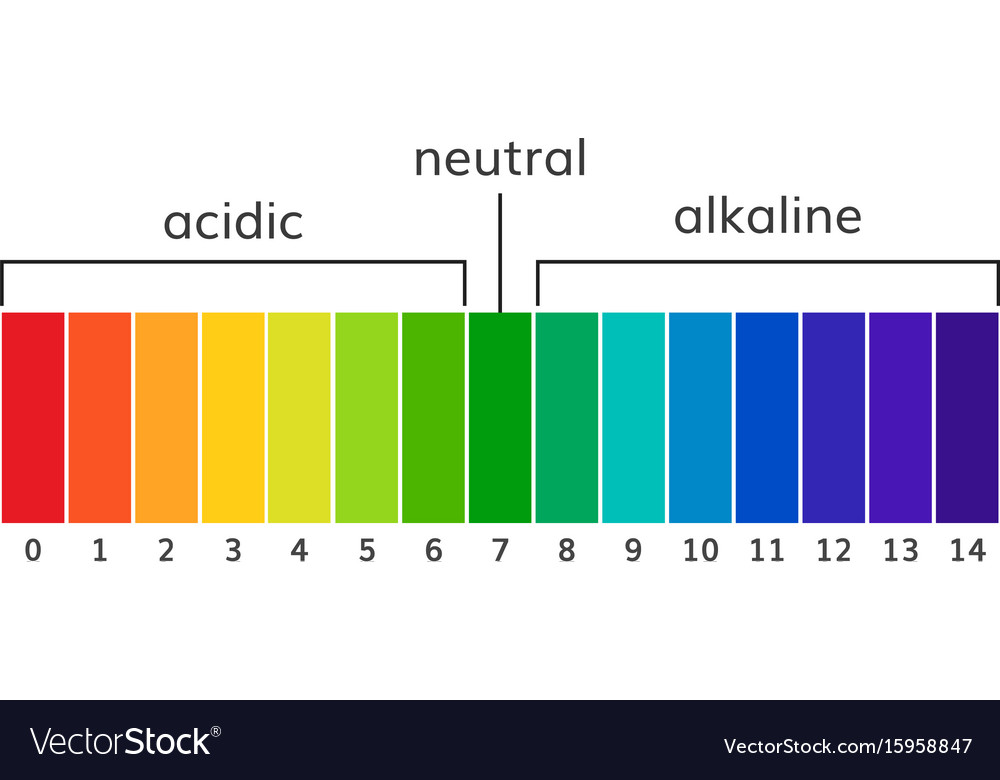
Chart ph alkaline and acidic scale Royalty Free Vector Image
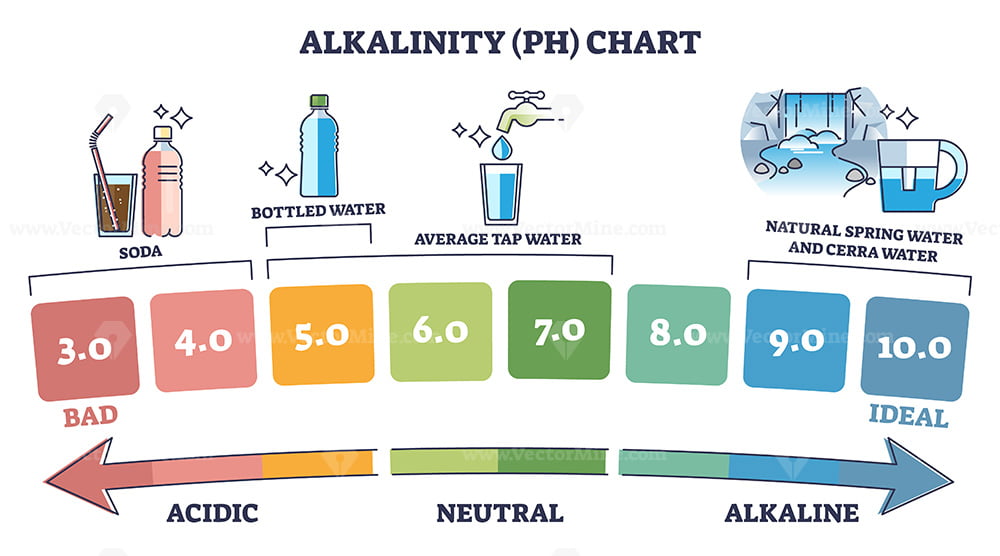
Alkalinity PH chart with water acidity from bad to ideal outline diagram VectorMine
Acid and Alkaline Chart Herbaldashery
Understanding Alkalinity and its Impact on Reverse Osmosis Membranes
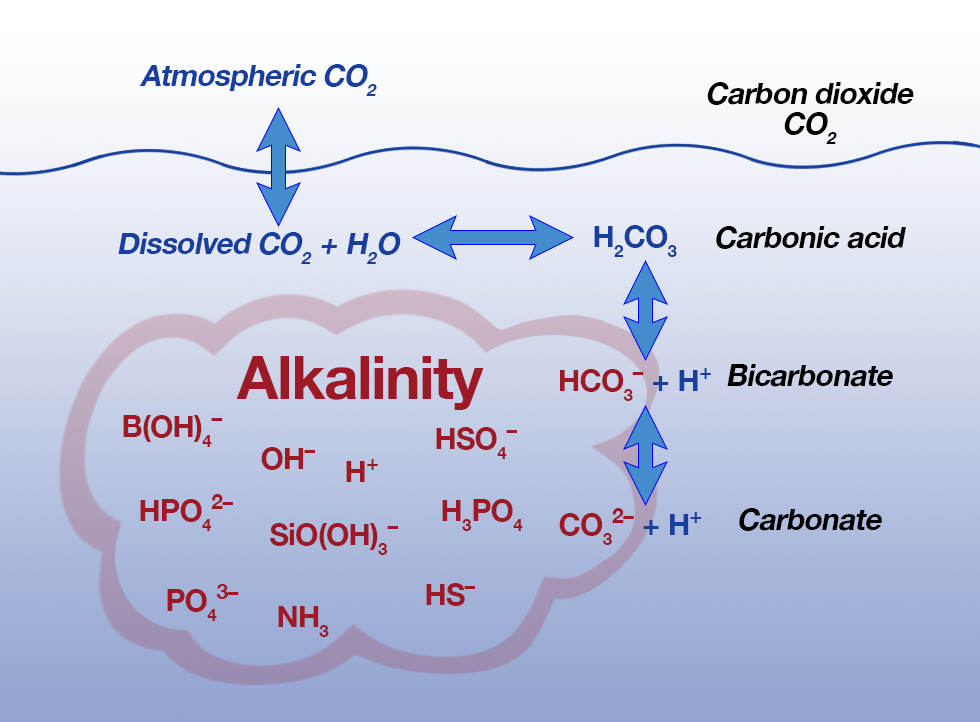
alkalinity measurement
Total Alkalinity PH, And Their Roles In Water Chemistry, 41 OFF
If Any Changes Are Made To The Water That Could Raise Or Lower The Ph Value, Alkalinity Acts As A Buffer, Protecting The.
Total Alkalinity Is A Measurement Of The Concentration Of All Alkaline Substances Dissolved In The Water That Can Both Attract And Release Hydrogen Ions (H +).
This Ability Is Usually Referred To As Water’s “Buffering.
It Is Measured By Titrating The Solution With An Acid Such As Hcl Until Its Ph Changes Abruptly, Or.
Related Post: